Investigation into the Truth Behind AI Server Shortages: Prices Soar by 300,000 in Two Days
-

Almost overnight, AI server prices have skyrocketed in the domestic market.
According to a server channel salesperson, popular AI server models equipped with NVIDIA A800 GPUs are now priced at 1.4 to 1.5 million yuan per unit, marking an increase of over 40% since June this year. The price surge for AI servers equipped with 8 NVIDIA H800 GPUs is even more staggering, jumping by hundreds of thousands of yuan in just a few days and nearing 2.8 million yuan per unit, an increase of over 10%.
Since the onset of the 'Hundred Models War,' the domestic AI server industry has experienced extreme highs and lows.
On one hand, the wave of large models has led to a surge in demand for AI servers. Internet cloud giants, AI model enterprises, and industry players are all investing heavily. Not only have ICT leaders like China Telecom recently allocated over 8 billion yuan for AI computing server procurement, but even cross-industry players like the 'MSG King' Lotus Health have jumped in, recently spending 700 million yuan to purchase GPU servers.
On the other hand, massive demand is struggling against insufficient supply. Popular AI server models have seen their prices multiply, with some costing nearly 3 million yuan yet remaining out of stock. Leading manufacturers such as Inspur, H3C, Nettrix, Lenovo, and Foxconn Industrial Internet have launched new models for large-scale AI applications, but when will these orders be fulfilled? That remains a big question mark.
AI servers are undeniably crucial for large models. If we compare a large model to a child that needs vast amounts of data to grow, then AI servers are the chefs determining whether the child gets well-fed. The 'Hundred Models Battle' is, in essence, a competition for AI servers.
As a bridge connecting chip manufacturers and large model enterprises, how can Chinese server manufacturers break through this bottleneck? This has become a critical issue for the development of China's large model industry.
'Previously, servers were hard to sell, but now it's the customers begging to buy!' a sales representative from a top server manufacturer told ZhiDongXi. 'Price hikes are secondary—many customers don’t even mind paying tens of thousands more. It’s clearly a seller’s market now. After signing a contract, we can’t fully guarantee the delivery timeline, nor do we promise penalties for delays.'
AI servers are heterogeneous, meaning their core chips can be configured in various combinations, such as CPU+GPU, CPU+TPU, or CPU+other accelerator cards. Compared to general-purpose servers, AI servers are better suited for the high computing power, concurrency, and data throughput demands of AI training and inference, making them the 'hot commodity' in the era of large models.
Taking the popular AI server model Inspur NF5688M6 as an example, one agent listed it at 1.25 million yuan on an e-commerce platform. This server, equipped with 8 A800 GPUs, was priced at 1.05 million yuan in May this year. Despite the nearly 20% price hike, it remains out of stock. Another online store with available stock priced the NF5688M6 at nearly 1.6 million yuan. A salesperson told ZhiDongXi that the现货 (ready stock) could be secured for 1.45 million yuan, but only two units were available, with more requiring bundled purchases of other brands like Ningchang or Supermicro.
▲Screenshot of the NF5688M6 server sales page on JD.com
Retailers informed ZhiDongXi that a new batch of AI servers based on H800 GPUs had arrived, but when asked about the price, they exclaimed how outrageous it was—increasing by hundreds of thousands in just a few days. Previously, the highest price was around 2.5 million yuan, but now it takes 2.8 million to secure one. Slower-reacting sales channels adjusted prices overnight, raising them by 300,000 yuan straight.
Regarding this year's market trends, server manufacturers and agents feel both surprised and overwhelmed. One manufacturer remarked to ZhiDongXi: "Every time we think computing power is about to become a 'red ocean,' it turns into an endless 'blue ocean.'"
This "blue ocean" sector has essentially received official endorsement from top authorities. On October 8, six departments including the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology jointly issued the "High-Quality Development Action Plan for Computing Power Infrastructure," proposing that by 2025, China's computing power scale should exceed 300EFLOPS (300 exaflops), with smart computing power accounting for 35%. According to data from the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology, as of the end of June this year, China's computing power scale reached 197EFLOPS, with smart computing power accounting for 25%.
This means the quantitative indicator for smart computing power will increase by over 110%, with an expected incremental market of about 56EFLOPS.
A representative from Inspur Information, a leading server manufacturer, told ZhiDongXi: "The rapid development of AIGC technologies, represented by large models, has brought unprecedented opportunities to AI computing. The rich application scenarios and enthusiasm for technological innovation have significantly increased the attention and demand for AI servers in the Chinese market, which is expected to maintain rapid growth in the coming years."
According to a previous report by the well-known research firm IDC, the accelerated server market reached $3.1 billion in the first half of 2023, a 54% increase compared to the first half of 2022. China's accelerated server market is projected to reach $16.4 billion (approximately 119.884 billion yuan) by 2027.
To tap into the "blue ocean" of smart computing power, intelligent computing centers that aggregate AI server clusters are a key focus. As shown in the chart below, from March to October 2023, over 10 super-large intelligent computing centers have been launched or are under construction across China, evenly distributed nationwide. Most operational centers are expanding while in use, further driving demand for AI servers.
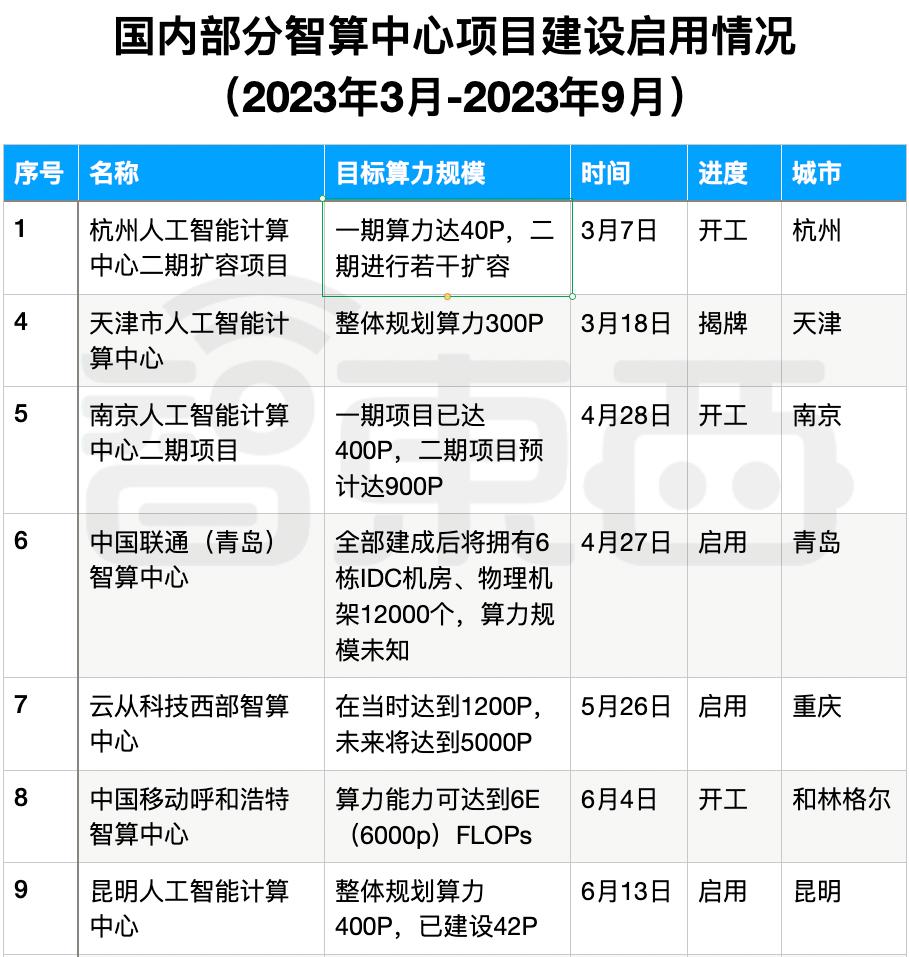
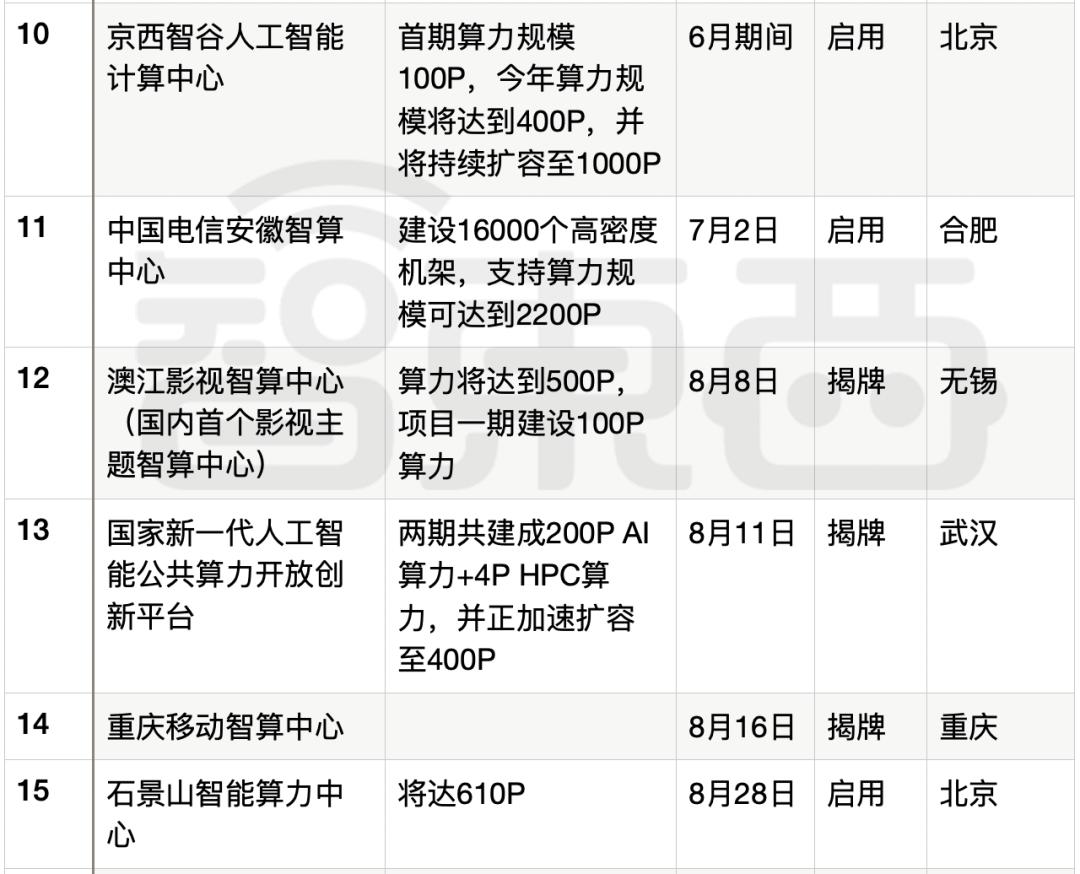

▲Status of some domestic intelligent computing center project constructions and launches
Behind the scenes, major internet cloud companies, telecom operators, AI model enterprises, and industry leaders have all joined the fray, placing consecutive billion-level orders with server manufacturers.
A senior executive from leading server manufacturer H3C told ZhiDongXi: "The deepening 'Hundred Models Battle' has led more enterprises, research institutions, and developers to adopt deep learning technologies, driving up demand for AI servers. Both training and inference phases require substantial computing resources, and AI servers provide the high-performance heterogeneous computing capabilities needed to meet these demands."
Recently, China Telecom completed the evaluation of bids for its AI computing power server procurement project (2023-2024), ordering a total of 4,175 training servers worth approximately 8.463 billion yuan. Companies including Hyperfusion, Inspur Information, H3C, Ningchang, ZTE, FiberHome, Lenovo, and several Huawei agents were selected as suppliers.
Even unexpected players like "MSG King" Lotus Health are joining the AI server buying spree. According to a procurement contract signed on September 28, H3C will deliver 330 Nvidia H800 GPU-powered computing servers (each containing 8 GPUs) to Lotus Technology Innovation, with the total contract value reaching 693 million yuan.
The market boom is evident - whether it's AI computing centers requiring dozens of petaflops or orders worth hundreds of millions, server industry players no longer worry about sales. Amid the large model wave, AI server business sees soaring prices, a promising market outlook, and expanding customer base, pushing manufacturers into a gold rush territory.
02.
Server Manufacturers Rush to Launch New AI Models, Orders Piling Up with Production Scheduled into Next Year
"Half of our orders are for AI servers, more than double the demand for traditional servers," a representative from a leading server manufacturer told Zhidongxi. "AI servers will remain in high demand for quite some time. The need for inference machines hasn't fully materialized yet—many clients are just testing the waters this year, but next year could see much heavier investment."
Recognizing large AI models as a long-term growth sector, agile server manufacturers have already rolled out new hardware tailored for these models.
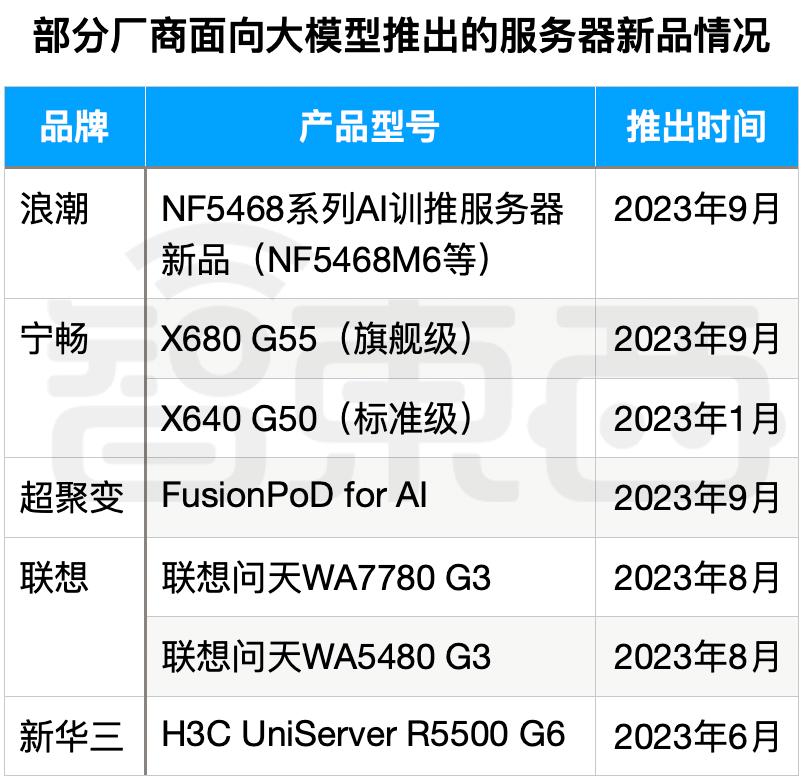
Compared to previous specialized small models, large model training has introduced numerous new requirements for servers. These include not only high-performance computing power, big data storage, and broader framework compatibility but also higher data transmission efficiency, improved fault recovery capabilities, and better AI computing cluster management. These demands are driving server manufacturers to develop new machines optimized for large model training and inference.
"Deep learning models are becoming increasingly large and complex, requiring greater computational power. This pushes AI servers to continuously improve performance, adopt powerful AI accelerators, and support higher bandwidth and larger capacities," a representative from H3C told ZhiDongXi. "To meet the demands of deep learning tasks, AI servers have spurred many design innovations. For example, improving computational density and efficiency has made thermal management, power consumption optimization, and green data center construction key considerations in server design."
H3C launched its large model-oriented AI server, the H3C UniServer R5500 G6, in June this year. It reportedly delivers 3x the computing power of its predecessor and reduces training time for GPT-4-like models by 70%.
As the industry leader with the top AI server market share for five consecutive years, Inspur Information also upgraded its NF5468 series AI servers on September 21, significantly improving fine-tuning performance for models like Llama. To achieve optimal performance, energy efficiency, or TCO (Total Cost of Ownership), industry-wide collaboration is essential. Since 2019, Inspur has led the development of the OAM (Open Compute Project Accelerator Module) standard and worked closely with chip manufacturers for compatibility. Recently, it released the next-generation OAM server NF5698G7, featuring full PCIe Gen5 connectivity and a 4x improvement in H2D interconnect capability.
A representative from Inspur Information stated that large models impose higher performance and functional demands on AI servers. The focus is not just on a single chip or server but on highly integrated AI computing clusters, which include computing, storage, networking, software, frameworks, model components, racks, cooling, power supply, and liquid cooling infrastructure.
Veteran server manufacturers like Lenovo are making comprehensive strategic moves to embrace the AI era. In August this year, Lenovo introduced two new AI server products: the Lenovo Wentian WA7780 G3 AI Large Model Training Server and the Lenovo Wentian WA5480 G3 AI Training and Inference Integrated Server. Concurrently, Lenovo unveiled its 'Puhui' AI computing strategy for the first time, committing to 100% AI support for its computing infrastructure products and allocating 50% of its infrastructure R&D investment to AI. The company also launched its Lenovo AI Computing Center solution and core service products.

▲ Introduction to Lenovo's two new server products
Chen Zhenkuan, Vice President of Lenovo Group and General Manager of the Server Business Unit of the China Infrastructure Business Group, emphasized that AI-oriented infrastructure must be designed and optimized based on the characteristics of AI data and algorithms. This includes addressing features such as the 'vector, matrix, or multi-dimensional array form' of AI data, 'high data noise,' and the 'massively parallel and matrix computations' and 'tolerance for low-precision floating-point or quantized integers' in AI algorithms.
Despite the fierce competition among server manufacturers to release new models for large AI models, only a few have managed to get their hands on the actual hardware. Many new AI server models are equipped with 8 H800, A800, or L40S GPUs. A representative from a related manufacturer revealed that new AI server orders are no longer being accepted, with previous estimates of a 6-month backlog now extending to 12 months.
Nevertheless, server manufacturers are accelerating their all-encompassing strategies, from software to ecosystem development.
An executive from Inspur Information told ZhiDongXi that unlike traditional small models, the capabilities of large models stem from extensive engineering experience. Therefore, while the current scarcity of computing resources may gradually be resolved next year, computing efficiency beneath the raw power remains another complex challenge.
Taking the pre-training phase as an example, first, the evolution of AI large models places high demands on cluster parallel computing efficiency, on-chip storage, bandwidth, and low-latency memory access. The planning, construction, performance tuning, and computing scheduling of 10,000-card AI platforms are all difficult problems to solve. Second, large-scale training commonly faces issues like hardware failures and gradient explosions, which are absent in small-scale training. Third, the lack of engineering expertise makes it hard for companies to rapidly improve model quality.
To address these challenges, Inspur Information is not only focusing on hardware deployment but also accelerating full-stack capability coverage through software algorithms. It recently launched OGAI (Open GenAI Infra), a large-model intelligent computing software stack introduced on August 24. This solution is said to provide AI computing system environment deployment, computing scheduling assurance, and model development management capabilities for large-model businesses, helping companies tackle system-wide computing issues, compatibility challenges, and performance optimization problems. Since 2019, Inspur Information has led the YuanNao Ecosystem Initiative, bringing together partners with core AI development capabilities and comprehensive industry solution delivery expertise.
▲ Introduction to Inspur Information's OGAI
Experts from H3C also believe that the 'Hundred Models Battle' has necessitated effective management and deployment of large-scale AI server clusters. To manage and deploy these servers, efficient cluster management software and automation tools are required to ensure high availability, performance, and efficiency.
To this end, H3C has developed a comprehensive AIGC solution by focusing on enabling platforms, data platforms, and computing platforms. In August, H3C's private domain large model, LinSeer, achieved a domestic-leading level of 4+ in the model development module during the large model standard compliance verification organized by the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology (CAICT). Additionally, H3C has strengthened collaborations with leading internet companies to explore deeper integration between private domain models and general models.
Moreover, manufacturers are competing to release industry reports, standards, and guidelines in an effort to establish authority in the field. For example, Inspur Information released the Open Acceleration Specification AI Server Design Guide, refining the full-stack design reference for AI chip deployment from nodes to clusters for AIGC. Meanwhile, Ningchang actively participated in AI server research projects and co-authored the AI Server White Paper.
It is evident that the rapid development of large models and AIGC technology presents unprecedented opportunities for AI computing, but also brings significant challenges that require multi-faceted responses in hardware, software, algorithms, and ecosystems.
AI servers have become a crucial battleground for server manufacturers—a competition for blue ocean markets and, more importantly, survival. Taking industry leader Inspur Information as an example, its 2023 revenue was 24.798 billion yuan, a year-on-year decrease of 28.85%, while net profit attributable to shareholders dropped by 65.91% to 325 million yuan. With limited growth in the traditional general-purpose server market, seizing the opportunities presented by intelligent computing power in the era of large models has become a critical step for server manufacturers to achieve new breakthroughs.
High Demand but Limited Supply: The Other Side of AI Server Boom
The explosive demand for AI servers is met with supply chain shortages, primarily due to insufficient supply. Nvidia has adapted to previous restrictions by supplying the Chinese market with modified versions of its flagship computing chips, the A800 and H800, which have reduced interconnect speeds. However, new regulations may impact the sales of these chips, and companies like AMD and Intel are also expected to be affected, further straining the domestic AI server supply chain.
GPGPU Dominance in AI Training
Industry insiders reveal that, for a long time, about 90% of large-scale models, both domestically and internationally, have been trained using GPGPUs, with only 10% relying on other ASIC chips. Among GPGPUs, Nvidia's A100, A800, H100, and H800 are the most efficient.
Adapting to Supply Constraints
Facing supply limitations, leading server manufacturers have continued developing GPU servers while adopting open architectures to accommodate domestic, innovative chips. For example, Inspur has introduced an open accelerated computing architecture, boasting high computing power, strong interconnectivity, and scalability. Based on this, Inspur has released three generations of AI server products, collaborated with over 10 chip partners to diversify AI computing solutions, and launched the AIStation platform, which efficiently manages more than 30 types of AI chips.
Alternative Approaches
Some server manufacturers are bypassing the GPGPU route and exploring innovative hardware solutions for AI servers. For instance, on August 15, iFlytek and Huawei jointly released the Spark One AI server, based on Kunpeng CPUs and Ascend GPUs, with Huawei providing storage and networking solutions. The server delivers 2.5 PFLOPS of FP16 computing power, compared to Nvidia's DGX A100 8-GPU, which offers 5 PFLOPS of FP16 power and is widely used in large model training.
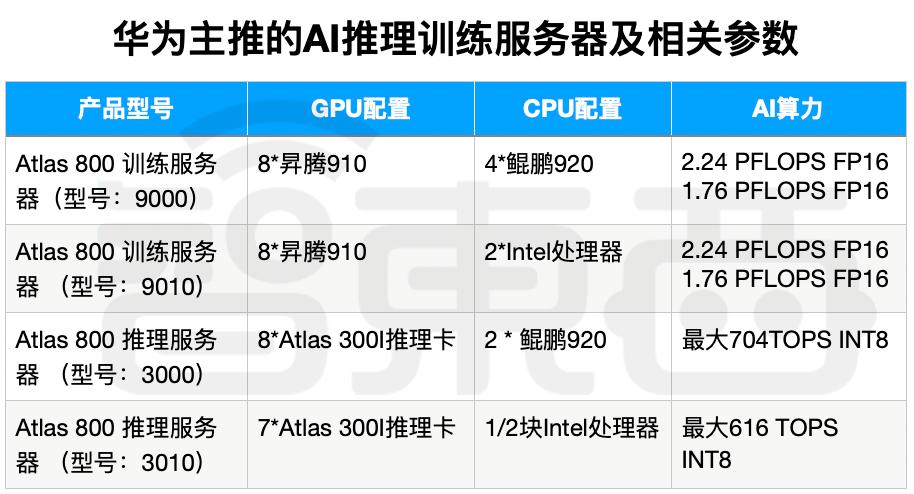
According to First Financial, the Spark integrated machine likely uses Huawei's yet-to-be-officially-released Ascend 910B AI chip, potentially positioned as a competitor to NVIDIA's A100. Huawei's publicly available Atlas server series already includes multiple inference and training machines, with the Ascend 910 slightly outperforming the A100 80GB PCIe version in specific large model scenarios like Pangu and iFlytek Spark.
However, industry sources reveal that the Ascend 910 is currently more suitable for large models within Huawei's own ecosystem, working best with its MindSpore framework, while lacking broader compatibility. Models like GPT-3 require significant optimization to run smoothly on Huawei's platform. Although partnerships with companies like iFlytek exist, much work remains in early stages.
Additionally, Hygon has independently developed two generations of DCU deep computing products now in mass production, offering strong support for general large model training and inference. Other domestic chip startups like Cambricon, Moore Thread, Biren, and MetaX are also supplying AI server manufacturers. Despite challenges, the current landscape is accelerating product iteration and deployment.
In summary, server manufacturers are adopting dual strategies to mitigate supply chain risks. Industry insiders note that while most domestic AI chip startups only began developing large-model-oriented chips in late 2022—making architectures and software ecosystems immature—faster iteration cycles could enable these chips to meet partial AI server demand by late 2023 or 2024.
With large models being implemented across industries, deploying AI computing power has become a vital direction for computing infrastructure development. IDC reports show that with the explosion of generative AI applications, the demand for intelligent computing in various sectors has surpassed that for general-purpose computing for the first time. AI computing power has become the main direction of computing development and a new strong driving force for the 'East Data West Computing' initiative.
The server industry and manufacturers play a crucial role in intelligent computing power construction. Currently, the domestic server market is witnessing soaring prices, approaching a red ocean, and expanding customer bases, while also facing severe risks such as supply chain shortages and supply-demand imbalances. At the critical juncture of the 'Hundred Models War,' AI server manufacturers are being tested on their ability to navigate the industrial chain. The key to breaking through lies in forming strong alliances with upstream and downstream partners while mitigating supply chain risks.
