How Do HR Professionals View the Transformation of Recruitment and Job Applications by AI?
-
Talent search and resume screening are the first steps in HR's recruitment process, often the most labor-intensive part—finding suitable candidates from vast resume databases, assessing their fit, and evaluating their potential for future roles. If AI takes over this workload, could it free up HR's time and energy? Suppose AI effectively evaluates every application before HR confirms the next steps—would this improve screening efficiency and reduce subjective biases?
To explore this question, a well-known international customer service company conducted a survey involving 1,068 participants, including HR professionals and non-HR individuals. The survey focused on the following key questions:
 What tasks do recruiters want AI to handle?
What tasks do recruiters want AI to handle?
 Are HR professionals afraid of losing their jobs due to AI?
Are HR professionals afraid of losing their jobs due to AI?
 Do people trust AI's role in recruitment?
Do people trust AI's role in recruitment?
 Can job seekers use AI to assist in their applications?
Can job seekers use AI to assist in their applications?
 What risks come with AI-driven recruitment?
What risks come with AI-driven recruitment?
 Can AI eliminate unconscious human biases?
Can AI eliminate unconscious human biases?
...
1. Nearly 67% of HR professionals believe AI has a positive impact on recruitment processes.
People think AI will free up HR's time (44%), provide valuable insights during recruitment (41%), and make HR's job easier (39%). However, some believe that using AI in recruitment may lead to overlooking unique and unconventional talents (35%) and have a negative impact on the HR industry (26%).
2. About 85% of HR professionals believe AI will replace certain aspects of recruitment in the future.
Around 15% of HR professionals think humans are irreplaceable and necessary throughout the entire recruitment process. Additionally, about 23% are concerned that AI will replace them in the recruitment process.

It is evident that most people believe AI tools will replace certain parts of the recruitment process, but the final stages will still be completed by the hiring team. While AI may be highly intelligent in performing tasks, it lacks the nuanced human touch and evaluation skills required in the final stages of recruitment. Human involvement is also necessary to build and maintain these AI systems.
The recruitment tasks most commonly expected to be replaced by AI include: screening candidates (63%), finding qualified candidates (56%), and posting job advertisements (46%). When automation is used to match candidates and document their data, the recruitment process becomes more accurate and cost-effective.
3. Approximately 77% of HR professionals believe AI will soon be advanced enough to take on the responsibility of hiring decisions, but only about 43% of job seekers share this view.
Surprisingly, as many as 56% of job seekers do not want AI involved in hiring decisions, while only about 23% of recruiters feel the same way.
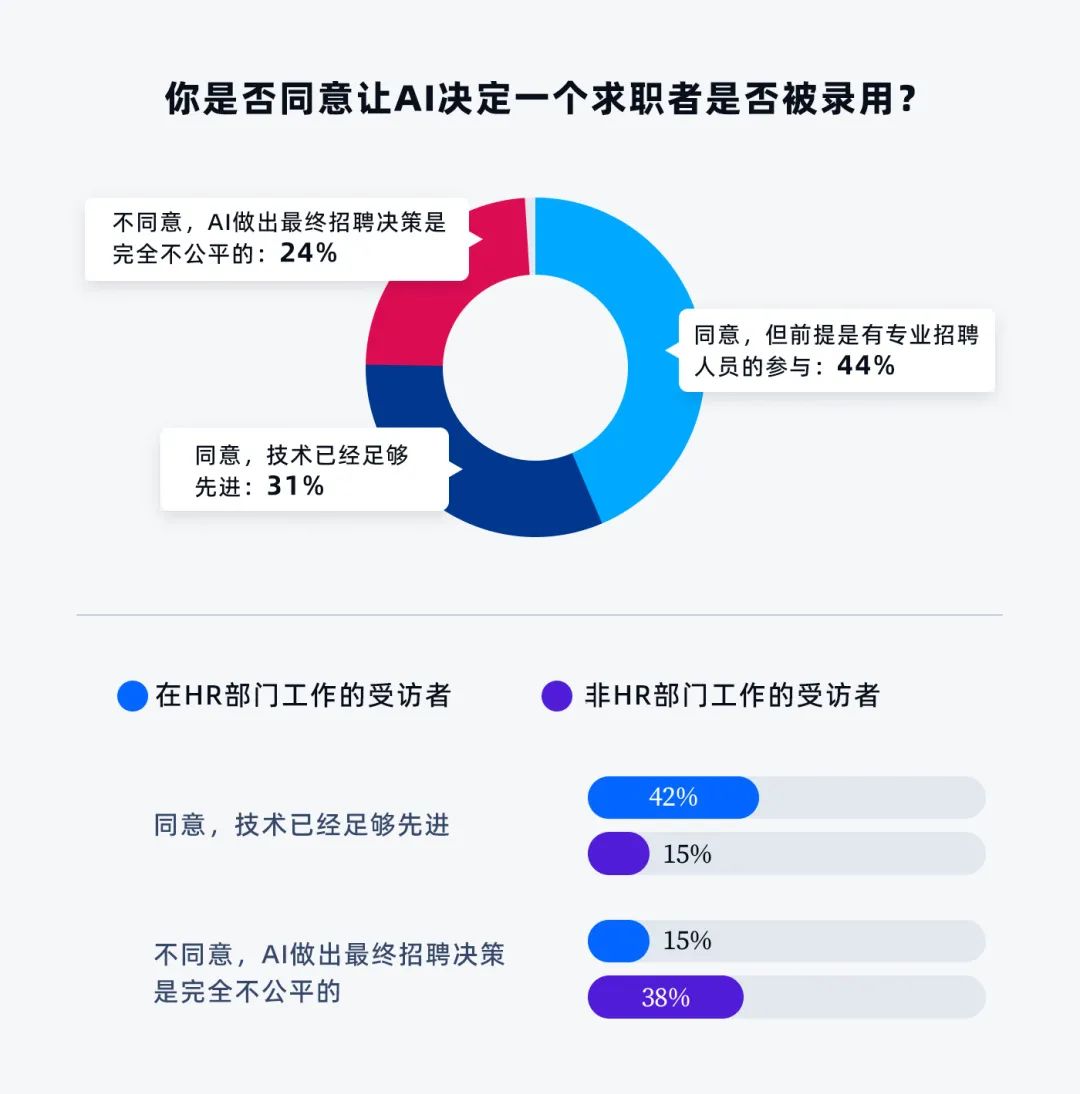
4. Only about 31% of respondents agree with the idea of AI deciding whether they are hired.
However, if human involvement is included in the decision-making process, this percentage increases to 75%. Only about 25% of participants believe it is entirely unfair for AI to make hiring decisions.
5. Approximately 89% of respondents believe AI can assist job seekers in completing application processes.
Only about 11% of participants think AI is useless for job seekers during the application process, while just 5% of HR professionals share this view.
1. Most respondents believe using AI in recruitment will eliminate unconscious bias or subjective misjudgment.
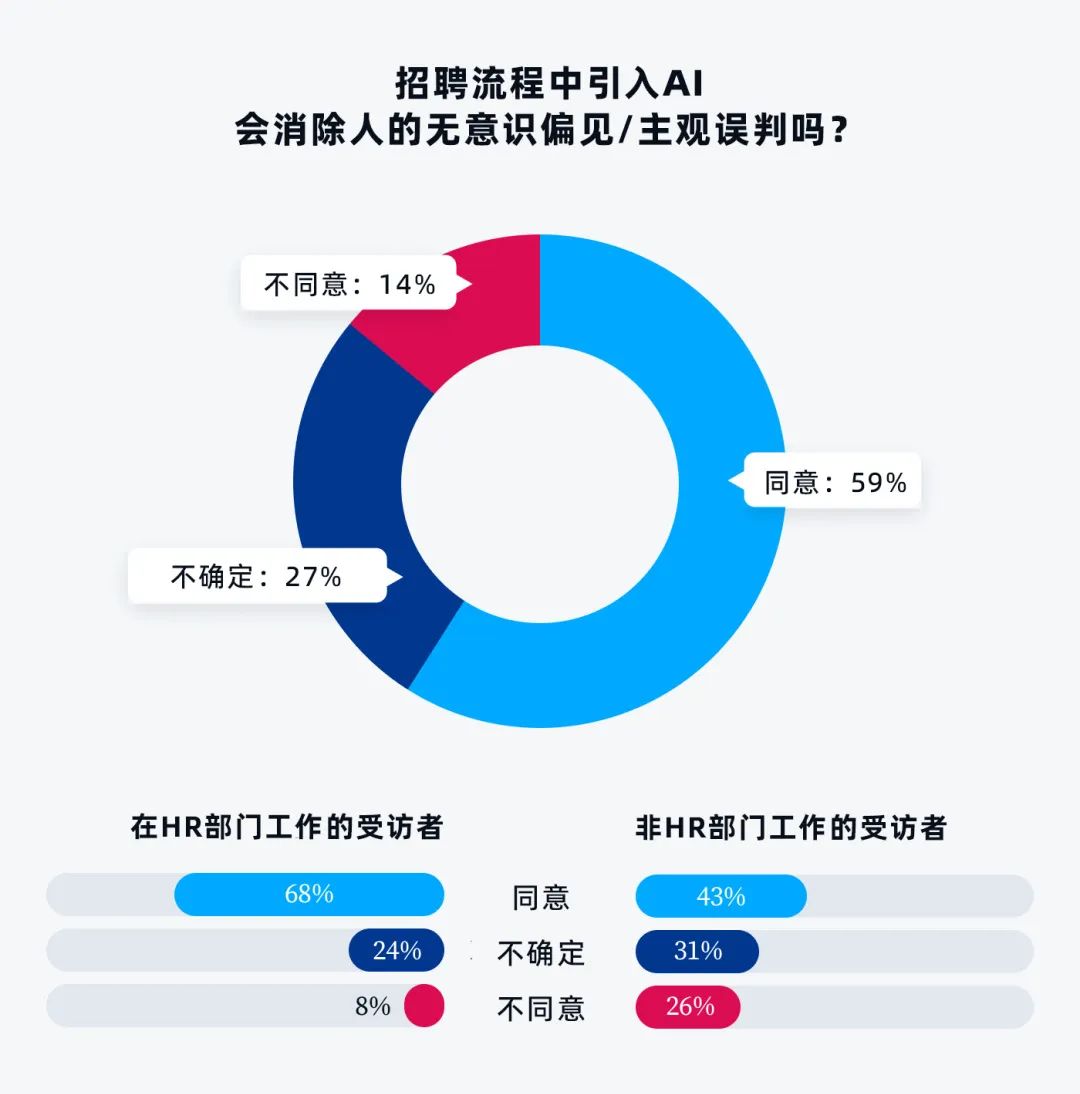
Some previous studies have found that AI can effectively eliminate unconscious bias by focusing on skills and candidates' experience. This undoubtedly helps create a more diverse workforce.
However, there are also examples showing AI has learned and amplified human unconscious biases. For instance, for positions traditionally held by men, AI algorithms may favor male candidates over females. Therefore, recruiters need to continuously monitor and train this technology to ensure it functions properly without bias.
2. AI can fully utilize its advantages to alleviate HR burden.
Research shows that HR professionals responsible for recruitment spend nearly one-third of their working hours searching for suitable candidates for a position. What is the most challenging aspect of this process for them?
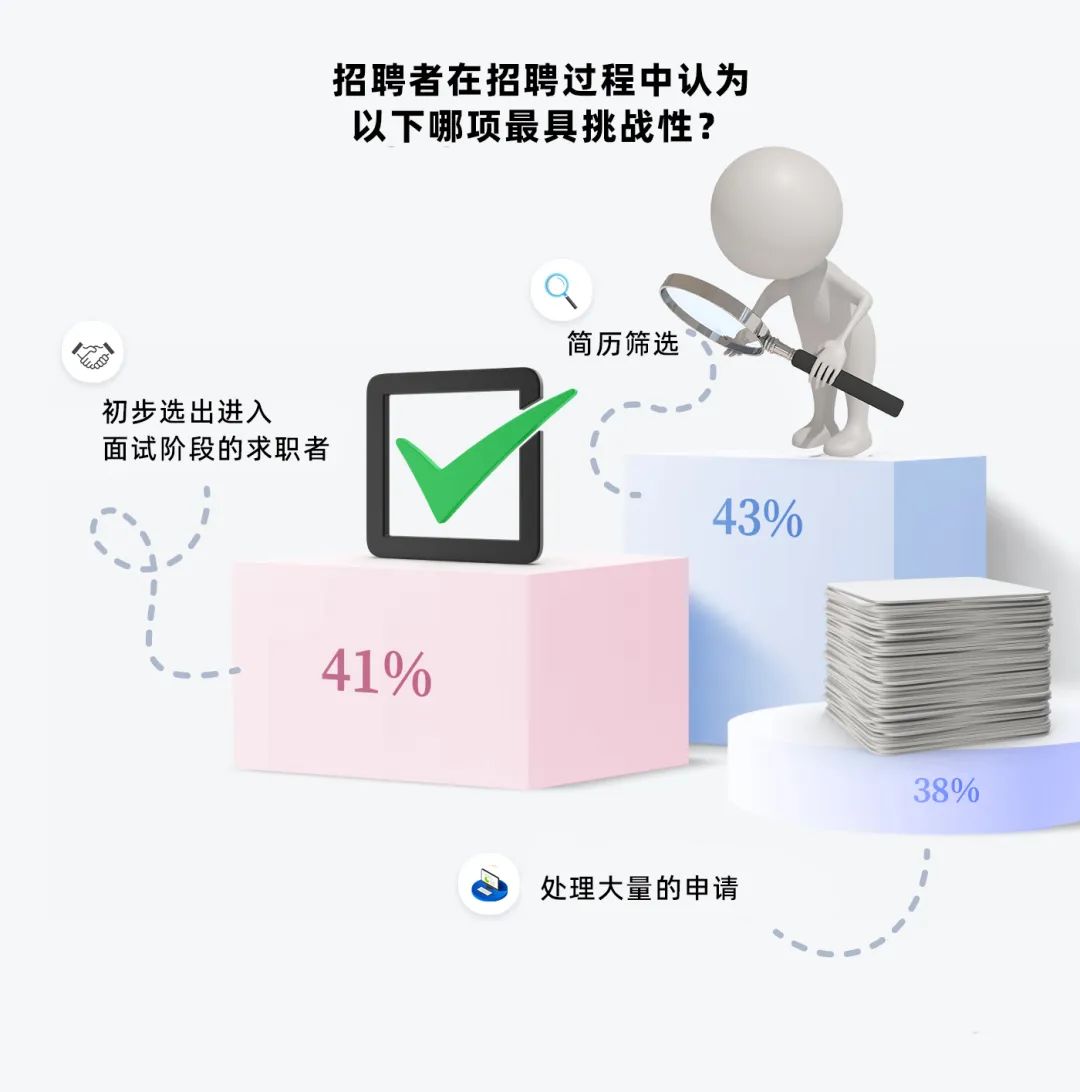
However, selecting candidates with the right experience and qualifications for the interview stage is indeed crucial. Introducing AI can alleviate these burdens for HR by assisting in resume screening and ensuring suitable candidates proceed to interviews.
3. Providing assistance to job seekers during the application process.
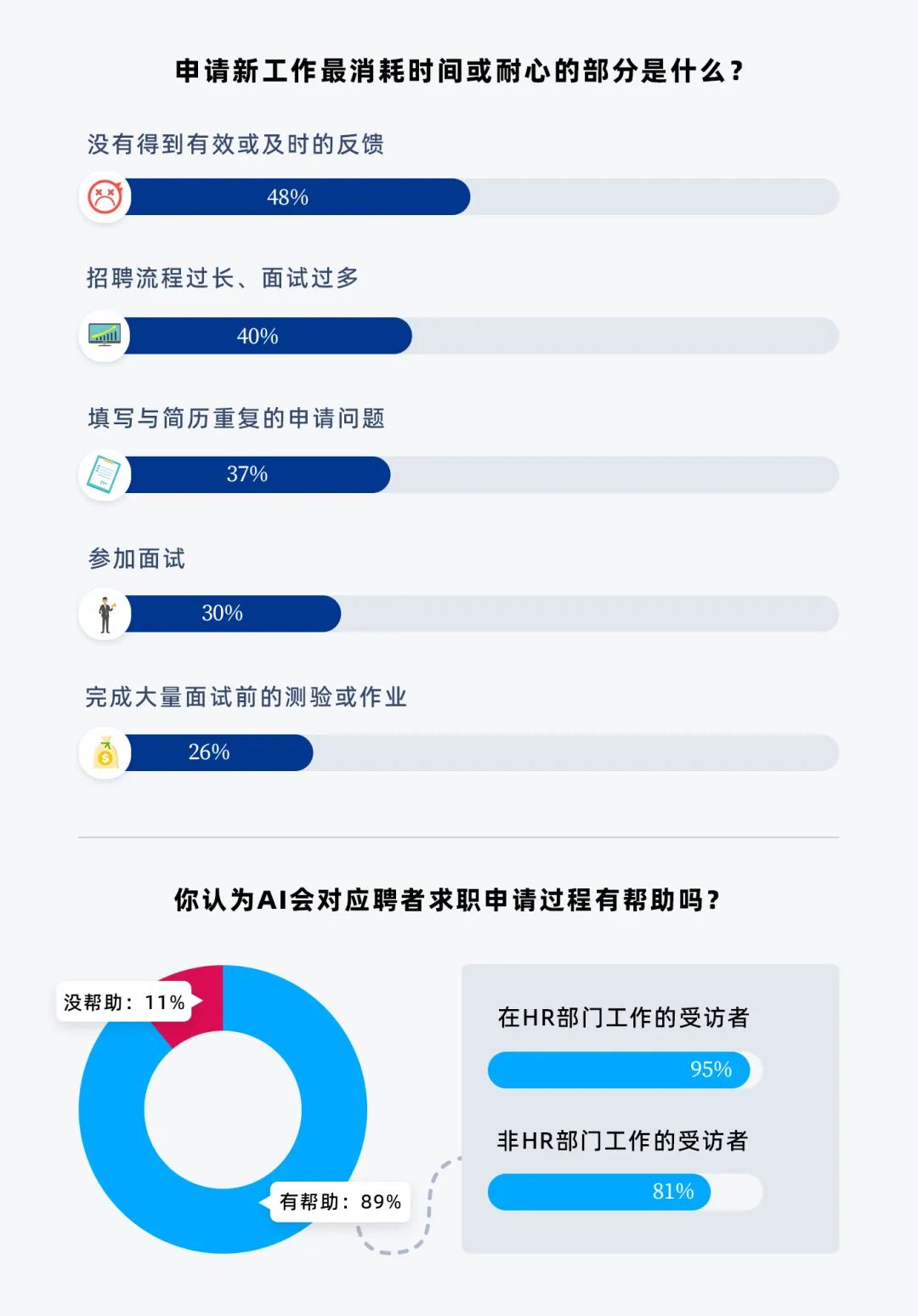
For job seekers, the most patience-consuming aspects of applying for new jobs often include not receiving timely feedback, dealing with numerous interviews, and sometimes having to fill out various application questions that repeat information already in their resumes.
In terms of giving/receiving feedback, AI can play a significant role—it can provide direct feedback after reviewing a candidate's application. Job seekers can also improve their chances of passing resume screenings by creating resumes that are optimized for applicant tracking systems (ATS). AI can also offer insights into whether a candidate is a good fit for a company.
Some of the best AI tools in the talent recruitment process include chatbots for answering frequently asked questions and ATS systems. These tools can enhance the quality and efficiency of recruitment, saving time on tedious tasks and better assisting HR professionals in achieving their goals.
Are there risks associated with using AI in recruitment? Survey results show that only about 13% of respondents are concerned about the inherent risks of using AI in the hiring process, while the majority (87%) believe there are some AI-related risks.

The survey also revealed that 44% of people would agree to let AI decide whether to hire them, but only if there is human involvement in the process.
The survey found that approximately 60% of respondents do not want their initial interviews to be recorded, though 35% would consent if given no alternative. Only about 40% of respondents trust AI's capability to analyze their body language during interviews.
Another study revealed that most people (53%) prefer recommendations from friends or colleagues over AI in the hiring process.
This distrust may stem from human biases, which AI could potentially replicate and amplify. Consequently, some regions have implemented regulations requiring companies to disclose their use of AI in recruitment and provide alternative options for applicants.
1. About 77% of HR professionals believe people will soon be completely excluded from the recruitment process.
A Forbes article from years ago argued that AI recruitment cannot operate as a 'black box'—it shouldn't be used without understanding its internal workings. This principle remains unchanged today. The technology requires ongoing evaluation and should primarily be used in the initial stages of recruitment. Human involvement remains essential in later stages where interpersonal relationships play a crucial role.
2. Over 90% believe AI is manipulable to some extent.
Among them, more than 46% think AI is easily manipulated. Only about 9% of respondents believe AI is advanced enough to resist manipulation.
AI's advantages include: saving time, avoiding bias, and improving candidate experience. However, its drawbacks are that it's not perfect and operates on relatively simple principles.
This technology can identify the most suitable candidates based on keywords in their application materials. But what if they've changed jobs several times in a year or aren't personality-wise suitable? That's when human recruiters need to step in.
3. About 76% of respondents said they wouldn't mind AI guiding their onboarding process.
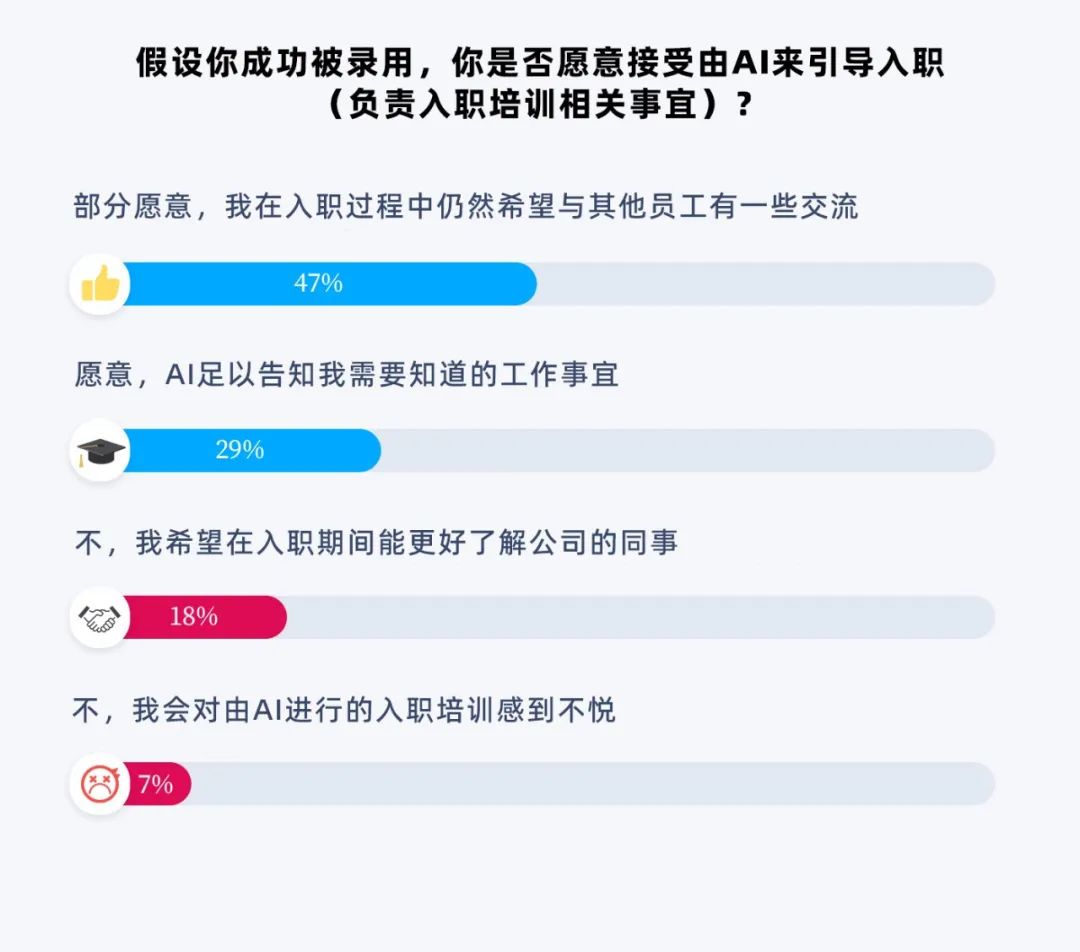
However, most new employees (about 65%) still hope to meet others in the company during the onboarding process. Among them, 47% are open to AI-assisted onboarding as long as they can interact with other employees, while 18% do not want AI involved in the process at all.
4. Over 87% believe AI is more useful in recruitment for certain industries than others.
Approximately 49% of respondents think AI recruitment is more effective in the computer and technology sectors. Only 7% believe it should be applied in advertising and marketing, and fewer than 7% consider it most useful in finance and economics.
A study published by the University of Texas found similar results. They concluded that the benefits of AI vary depending on the job seeker's role and the type of decision-making assistance the system provides. Therefore, when considering whether to use AI in recruitment, companies need to evaluate its application in their industry to understand its advantages and disadvantages.
