Generative AI Could Add $2.6 to $4.4 Trillion Annually to the Economy
-
October 9 News: According to a report by global consulting firm McKinsey, the AI industry could add $2.6 to $4.4 trillion annually to the economy in the coming years. This massive economic contribution prediction for the AI industry is based on two independent analyses: one examining the impact of AI on work activities across over 800 occupations, and another focusing on specific use cases where AI can benefit organizations.
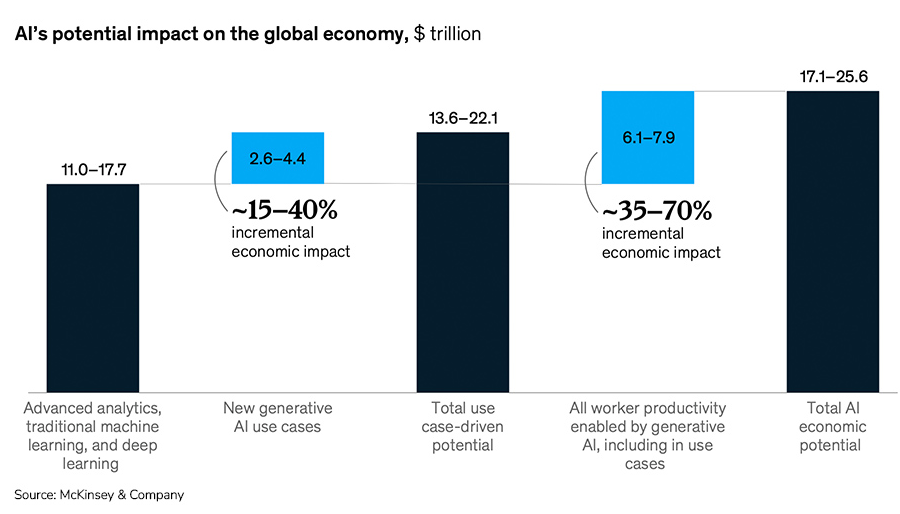
The report states: "We identified 63 generative AI use cases spanning 16 business functions, which, when applied across industries, could generate economic benefits of $2.6 to $4.4 trillion annually." For reference, the GDP of the UK, Europe's second-largest economy, totals $3.1 trillion.
The report predicts that AI tools—particularly generative AI tools like ChatGPT—will automate nearly all types of work between 2030 and 2060. McKinsey had previously forecasted that AI would automate about half of all work between 2035 and 2075, but the recent explosive growth of powerful generative AI tools has significantly accelerated this timeline.
The general perception of artificial intelligence tends to assume that AI primarily replaces low-level and repetitive jobs. However, reports indicate that AI will have a more substantial impact on high-paying, highly educated knowledge workers. These types of jobs were previously considered to have the lowest potential for automation, but studies now show that the higher the education level, the greater the influence of AI technology.
McKinsey states, "Generative AI is likely to have the most significant impact on knowledge work, particularly activities involving decision-making and collaboration, which were previously seen as having the lowest automation potential."
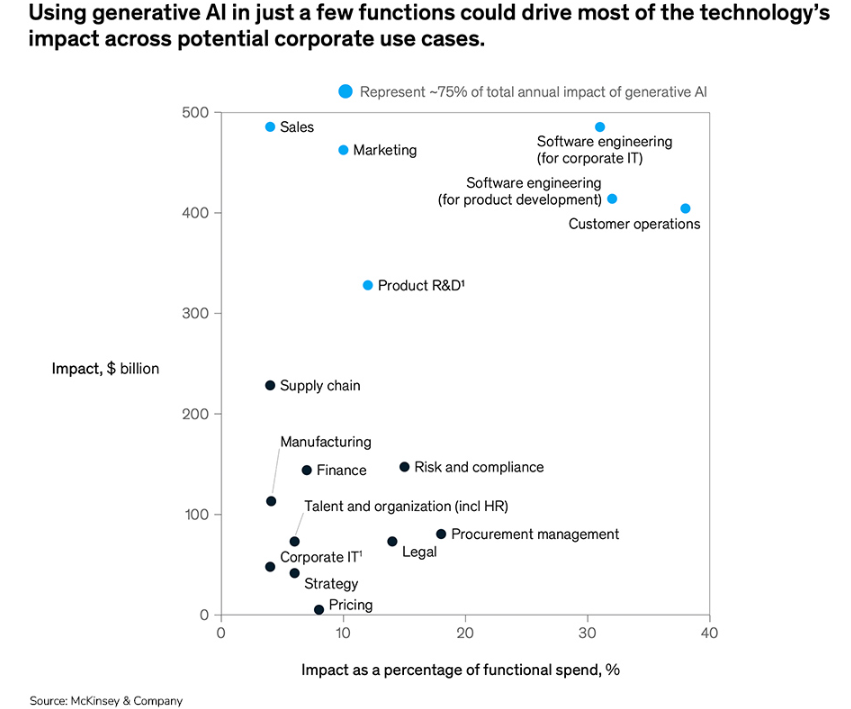
Generative AI has the potential to revolutionize how organizations manage internal company information, making it easier for employees to access archived data through ChatGPT-like query interfaces. As a result, these emerging generative AI tools are best suited for industries such as sales, marketing, software engineering, and customer operations.
Due to higher wages making automation more economically viable in the short term, automation is expected to proliferate faster in wealthier nations. Compared to high-wage countries like the U.S. and Germany, lower-wage nations such as China, India, and Mexico are anticipated to adopt automation at a slower pace.
While there is much to be optimistic about, there are also reasons for caution regarding the rapid adoption of AI technology across multiple industries. With the swift advancement of AI, some experts have begun expressing concerns about potential risks.
Beyond job displacement, other issues include harmful algorithmic biases and security vulnerabilities related to personal data. Some countries and regions have already started seeking regulatory measures for the industry. For example, the European Union has been working on AI regulations, including the AI Act initially proposed by the European Commission in 2021.
