The AI-Driven Device Upgrade Wave is Inevitable - The Next AI Tipping Point
-
One year after the release of ChatGPT, the generative AI frenzy has swept through tech companies. Smartphone and PC manufacturers are racing to integrate AI into their products, rapidly ushering in a new round of hardware competition.
Since Huawei integrated its Pangu model into smartphone assistants in August, Xiaomi, OPPO, Vivo, and Honor have quickly followed suit. Generative AI has become an essential selling point for new device releases in the coming years.
While smartphone manufacturers are rushing to implement large models, PCs have also begun their own AI revolution. Microsoft, the first to propose "Copilot," has already integrated OpenAI's large models into its operating system and productivity tools.
As generative AI accelerates its shift from the cloud to end-user devices, the demand for AI processing capabilities is driving rapid upgrades in hardware architectures.
On the mobile front, Qualcomm's Snapdragon 8 Gen 3 processor released in the second half of the year can already support running large models with up to 10 billion parameters. It takes only 0.6 seconds to generate a high-quality image, outperforming many domestic large models in both speed and quality.
On the PC side, Intel unveiled its next-generation Core
 Ultra processor codenamed Meteor Lake at the "AI Everywhere" launch event today, featuring a built-in AI acceleration engine NPU for the first time.
Ultra processor codenamed Meteor Lake at the "AI Everywhere" launch event today, featuring a built-in AI acceleration engine NPU for the first time.
Unlike cloud training scenarios, the inference phase of large models doesn't require extremely demanding computing resources. However, integrating more advanced models increases challenges for chip computing power, memory bandwidth, and battery efficiency. For end-users to fully experience the qualitative changes brought by AI, cost and differentiated experiences remain the most significant variables.
这其中,就是各家设备商们可以各项神通的演武场。
他们等这样一个机会,等了太久。
**AI大模型对于智能终端带来最大的帮助,体现在交互价值上。**近几年终端一直缺少这种颠覆性的变化,所以当Open AI拿出以GPT为底座的ChatGPT,不少人感觉好像回到了2007年iPhone问世的时刻。
落地终端最清晰的终极愿景,就是AI Agent,看过科幻片的都懂。

Lenovo CEO Yang Yuanqing defines this as: Large models deployed on edge devices use personal data stored in local servers for inference. Devices integrated with large models become digital extensions of users - by learning and mimicking our usage patterns, they evolve into intelligent companions called 'AI Twins'.
Before the AIPC concept emerged, smartphone assistants were also marketed as intelligent features by manufacturers. In reality, they were merely programmed mechanical Q&A systems - like 'idiot assistants' that simply occupied our device memory.
The birth of GPT made humanity realize for the first time how smooth communication with an intelligent assistant could be. With the capabilities of large models in retrieval, analysis, and logical reasoning, we can now interact more naturally and casually with AI assistants and assign more complex instructions.
First, timeliness determines the significance of many application scenarios. Edge AI relies solely on device processors for support, enabling smooth operation even in offline or weak-network conditions, eliminating issues like network latency.
At the same time, our text messages, photos, chat histories, memos, and schedules form a vector database that large models can retrieve. Without requiring retraining, these can be combined with text generation capabilities to produce final outputs. Moreover, this data does not need to be uploaded to the cloud during processing, ensuring privacy and security.
Additionally, multimodal capabilities can deliver rich interactive experiences for users. The generalization abilities of large AI models in natural language processing, image recognition, and speech recognition can create more imaginative application scenarios on devices.
For example, VIVO's Xiao V, integrated with the Blue Heart large model, allows users to manage tens of thousands of photos on their phones by using semantic recognition. Users can verbally describe the content of photos, and Xiao V will actively identify and retrieve the corresponding images from the album.
From the manufacturer's perspective, user experience and cost directly affect the extent to which device manufacturers engage with large model technology.
First, the training and inference of general large models in the cloud are highly resource-intensive. Beyond computing power, data transmission consumes significant resources such as network bandwidth and storage. The computing costs alone in the cloud are already expensive for startups like OpenAI, with ChatGPT's monthly user access maintenance costs reaching $10 million.
Their investment in an AI hardware company's first-generation product, AI Pin, requires a $24 monthly subscription fee to access AI features. For users who almost never subscribe to any services on their phones, convincing them to pay extra for an AI assistant is nearly impossible.

Smartphone manufacturers are hesitant to fully invest in immature technological applications. In contrast, edge devices act like "capillaries," sharing some computational loads with central nodes. The synergy between "cloud" and "edge" may be crucial for accelerating the widespread application of large models.
Some manufacturers like Huawei, VIVO, and OPPO are pursuing this cloud-edge collaborative approach, developing model matrices ranging from billions to hundreds of billions of parameters. By combining parameter scale with hardware characteristics, smartphones may achieve differentiated features.
In Huawei's demonstrations, users can already interact naturally with Xiaoyi (their AI assistant) to express needs, while Huawei's meta-services then launch relevant apps to fulfill these requests.
Meanwhile, Xiaomi is primarily focusing on on-device large models, having recently successfully run a 1.3 billion parameter model locally on smartphones, with some results comparable to 6 billion parameter models running in the cloud.
If large AI models can eventually standardize interfaces to access all device functions, applications may no longer need to design their own interfaces in the future. AI assistants would become the human-computer interaction interface, serving as the gateway to all applications. At that point, the relationships between users and interfaces, device manufacturers, operating system developers, and third-party applications would all be reshaped.
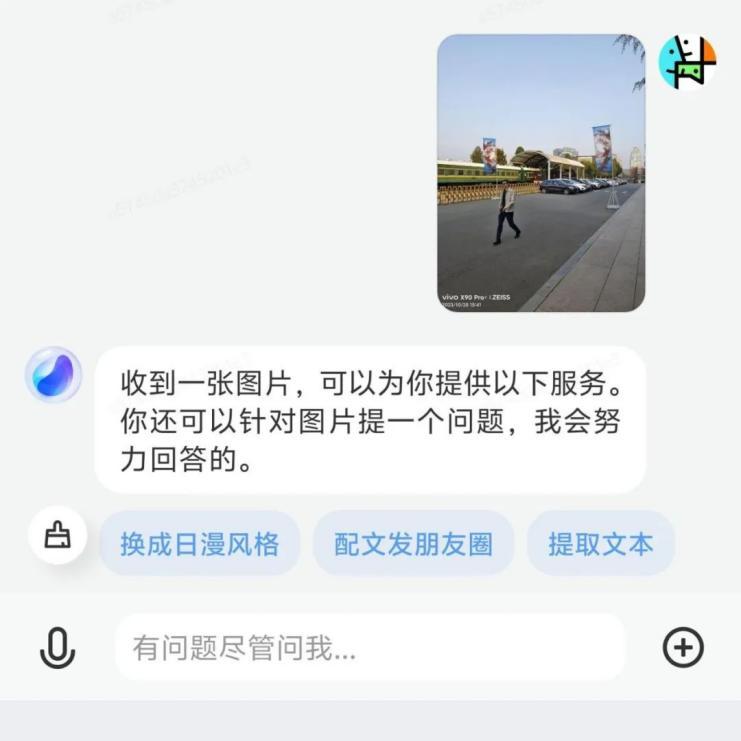
Industry veterans are urgently seizing this long-unseen opportunity. According to Intel, AI PCs will account for 80% of the PC market by 2028.
IDC predicts that the adoption rate of AI PCs (excluding tablets) in China's PC market for new devices will increase from 8% this year to 85% by 2027. The corresponding market size is projected to grow from 14.1 billion yuan in 2023 to 131.2 billion yuan in 2027, representing an increase of over 8 times.
However, there is a prerequisite: the edge side must first solve how to compress large models to a scale suitable for terminals while ensuring that core capabilities are not lost.
For device manufacturers, this is a major challenge but also a great opportunity. Whoever solves it first will be the first to reap the most substantial benefits.
One solution is to improve the performance of small models, focusing on being small yet powerful.
For example, Microsoft's recently trained Phi-2, with 2.7 billion parameters, has almost outperformed all large models below 130 billion parameters in tests, including Google's latest Gemini Nano 2. Compared to the 25-times larger Llama-2 model, it even performs better in multi-step reasoning tasks (such as coding and mathematics).
For AI PCs, traditional CPU-centric computing architectures can no longer meet the parallel computing demands of AI neural networks. Intel has proposed an "XPU" solution, combining CPU, NPU, and GPU. This leverages the NPU's high efficiency and low power consumption, the CPU's suitability for lightweight single inference tasks, and the GPU's high-throughput parallel computing capabilities to flexibly address diverse AI computing needs.
It's reported that Microsoft's Copilot-integrated PCs require a minimum computing power of 40TOPS. Qualcomm's new PC processor, the Snapdragon X Elite, delivers 75TOPS through its integrated AI engine.
AMD's upcoming Ryzen 8000 series, set for release in 2024, will also meet these performance standards.
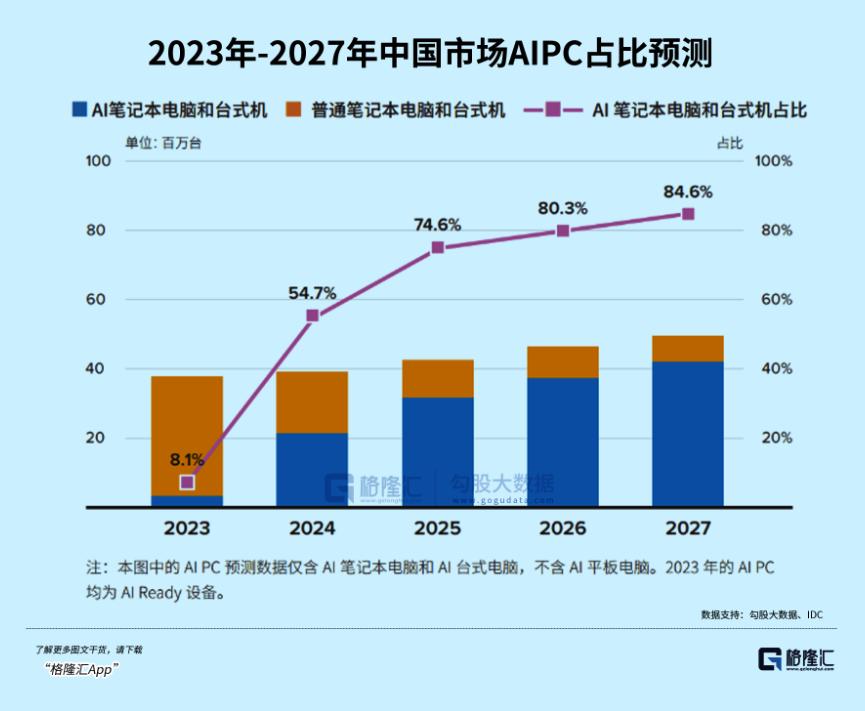
However, the vision of "AI for everyone" remains largely aspirational at present. Beyond accelerated processors, AI functionality demands additional hardware upgrades including high memory bandwidth and low power consumption. Whether end devices can run large models with tens or hundreds of billions of parameters depends not just on processing capability but also on whether the memory can accommodate them.
Most computers today come with 8GB of memory, but running a large language model with 7 billion parameters at 16-bit precision requires at least 14GB of memory. A feasible solution is to reduce memory usage through model quantization and compression. A 7-billion-parameter model, when quantized, can be reduced to approximately 2GB-4GB of runtime memory, making it possible to run on mobile devices.
Meanwhile, most smartphones and PCs have data transfer speeds below 1GB/s, with the fastest PC storage drives reaching up to 6GB/s. At 1GB/s and 4-bit quantization, only models of around 2 billion parameters can be run efficiently.
However, from another perspective, this presents a monumental opportunity for device manufacturers in this era.
Because the AI-driven device replacement wave is bound to occur.
Whether it's smartphones or PCs, the resulting market scale will be enormous.
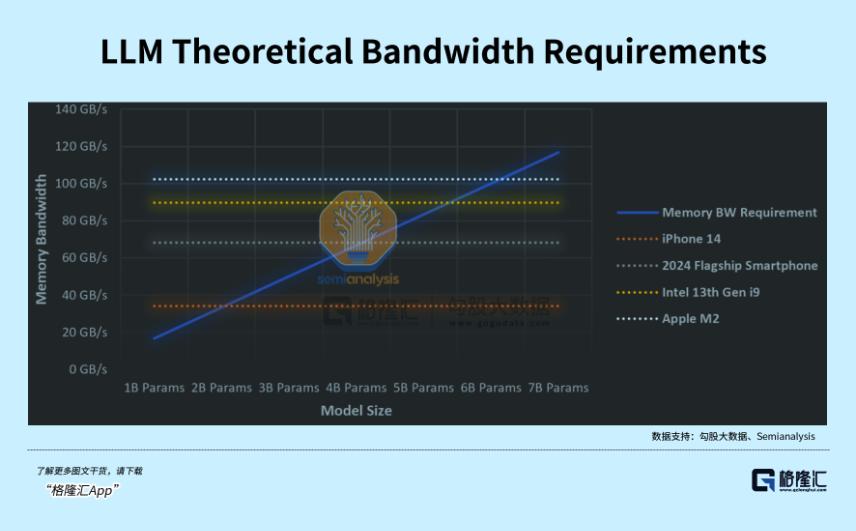
Personal computers and smartphones entered a saturated market in 2011 and 2016, respectively. After 2020, due to increased demand for remote work, the overstretched demand pushed PC shipments to a peak of 340 million units in 2021. Since then, demand has remained sluggish, shipments have plummeted, and inventory has piled up. The natural replacement cycle for traditional PCs lacks the driving force of technological innovation.
According to IDC, global PC shipments in the first three quarters of this year fell by 17.1% year-on-year to 187 million units, dropping to levels seen in 2005.
After two years of adjustment, the personal PC market has reached the bottom in terms of shipment volume and inventory cycle, with a new replacement cycle just around the corner.
On one hand, global PC shipments in Q3 increased by 11% quarter-on-quarter, with the year-on-year decline narrowing to 7.6%. After more than a year of inventory reduction, mainstream manufacturers such as Lenovo, HP, and Dell have now reached relatively healthy inventory levels, with the destocking process nearing its end.
On the other hand, Windows 10 will cease updates in 2025, and the new system with Copilot may require higher-specification computers. According to information disclosed on Microsoft's official website, Windows 10 will stop receiving updates on October 14, 2025, after which personal computers running only Windows 10 or lower system configurations will face compatibility challenges.
Gartner believes that the personal PC market has bottomed out, with inventory gradually returning to normal levels due to seasonal demand in the education sector and holiday sales. The global PC market is expected to grow by 4.9% in 2024.
Currently, Intel is collaborating with over 100 software vendors to bring hundreds of AI-enhanced applications to the PC market. These highly creative, productive, and entertaining applications are set to transform the PC experience.
Previously, NVIDIA's Jensen Huang also stated: "The PC industry is facing a rebirth opportunity. In the next 10 years, new AI PCs will replace traditional PCs, creating a market worth trillions of dollars."
With industry leaders making such statements and taking action, if we remain indifferent to this sector, we may miss another rare opportunity.
