In the Era of Large Models, Tech Giants Rush into the AI Chip Race
-
Since the explosion of ChatGPT, NVIDIA has not only been recognized as the biggest 'shovel seller' in the global AI gold rush but also the most discussed AI chip company across major media and social platforms.
Recently, NVIDIA's Q3 2024 financial report showed record-breaking revenue of $18.12 billion, a 206% year-over-year increase and a 34% quarter-over-quarter growth. Net profit also hit a new high at $9.243 billion, up 1259% year-over-year and 49% quarter-over-quarter.

However, in the tech world, no single company can dominate forever. As the AI boom continues to heat up, more manufacturers are entering the AI chip arena. Downstream clients like Amazon Web Services, Microsoft, Huawei, and Baidu are pushing for self-developed chips, while smaller but innovative AI chip unicorns like Cambricon and Biren are fiercely competing for a ticket to the AI era.
This year, multiple domestic companies in China are developing their own large AI models. Fearing potential escalation of US chip export controls that could cut off supplies of Nvidia's high-performance computing chips, Chinese internet companies have no choice but to compete in stockpiling A800 chips, as none want to fall behind in the artificial intelligence race.
Insiders reveal that Baidu, ByteDance, Tencent, and Alibaba have placed $1 billion orders with Nvidia for approximately 100,000 A800 chips to be delivered this year. Additionally, they've ordered $4 billion worth of chips for delivery next year.
This development has made Nvidia the biggest winner in the generative AI field. With its highly sought-after GPUs becoming 'scarce as gold' in generative AI, Nvidia has reaped enormous profits, with its market value soaring to $1 trillion. A Bloomberg report indicates that with the emergence of services like OpenAI's ChatGPT, the generative AI market is expected to surge from $40 billion in 2022 to $1.3 trillion within the next decade, attracting more players to the industry.
It is well known that developing proprietary AI chips is an inevitable trend for maturing industries. Whenever a manufacturer's AI computing volume increases substantially, custom chips become necessary to achieve optimal performance.
Especially in the era of digital economy, given the unprecedented market prospects in artificial intelligence, building proprietary chip supply chains has become a strategic focus for global tech giants. It's inevitable for software and cloud service leaders like Google, Microsoft, and Amazon to join the chip competition.
On December 1, Amazon Web Services (AWS) announced at re:Invent 2023 the next generation of its custom chip family, including Amazon Graviton4 and Amazon Trainium2, providing better cost-performance and energy efficiency for diverse workloads like machine learning training and generative AI applications. Compared to the current Graviton3 processor, Graviton4 delivers up to 30% better performance, while Trainium2 offers 4x faster training speeds than its first-generation predecessor.

On November 15, Microsoft unveiled the Maia AI accelerator chip at its Ignite developer conference in Seattle. Designed specifically for running large language models, the Maia chip features a distinct network connectivity approach compared to Nvidia's solutions, utilizing standard Ethernet cables for interconnection.

Earlier on August 29, Google announced its fifth-generation custom Tensor Processing Unit (TPU v5e) during the Google Cloud Next conference in San Francisco. This AI chip demonstrates significant improvements - delivering 2x better training performance per dollar and 2.5x better inference performance per dollar compared to its predecessor.

Metaverse New Voice believes that chips will likely remain the core of AI competition for a long time to come, involving nations, tech giants, and startups alike. However, the industry is still in its infancy, and a major reshuffle is inevitable in the future.
With intensifying global competition, China's AI chip industry is entering a critical period of opportunity.
Data shows that in 2021, China's AI chip market reached 42.7 billion yuan, a 124% year-on-year increase. In 2022, the market size doubled again to 85 billion yuan. China Post Securities predicts that by 2023, China's AI chip market will further expand to 120.6 billion yuan.
In fact, China places high importance on the development of the AI chip industry, having implemented a series of supportive policies to create a favorable regulatory environment and accelerate rapid industry growth.
In recent years, the Chinese government has successively introduced multiple policies to encourage the development and innovation of the AI chip industry, including the "New Generation Artificial Intelligence Development Plan" and the "Notice on Several Policies to Deepen Mass Entrepreneurship and Innovation."
Key cities such as Beijing, Shanghai, and Shenzhen have also released policies to support the rapid development of the artificial intelligence industry. These policies focus on breakthroughs in AI chip innovation, strengthening R&D in AI chips and smart sensors, and accelerating the construction of intelligent computing power.
NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang once stated, "China has many GPU startups. Don't underestimate China's ability to catch up in the chip field."
From the current landscape of domestic chip manufacturers, there are giants like Huawei advancing across the entire industrial chain, companies like Cambricon focusing on AI computing power chips, and others like Moore Threads specializing in general-purpose computing chips. This reflects the "blooming of a hundred flowers" in the domestic chip industry while supporting the increasing intelligence of large models.
Not long ago, Huawei unveiled its newly architected Ascend AI computing cluster—Atlas 900 SuperCluster—at its Connect conference. It is reported that this AI cluster supports large-scale model training with trillions of parameters and adopts a brand-new intelligent computing switch and super-node architecture.
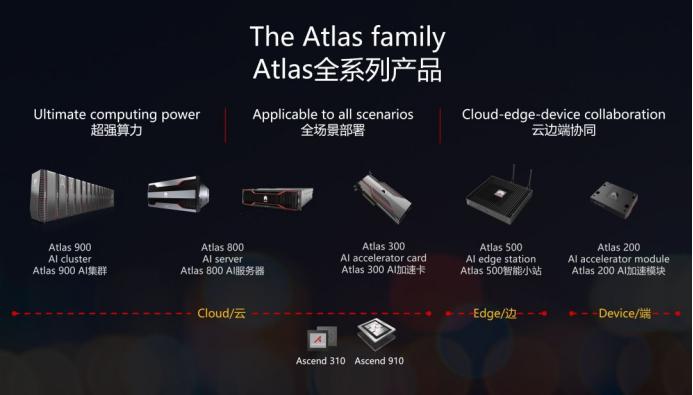
In an interview with Ren Zhengfei, he mentioned that Huawei's current AI cluster capabilities are no weaker than those in the U.S. "Huawei's current AI cluster already supports 16,000 boards, and a future super-node cluster will be able to manage hundreds of thousands of boards. It supports ultra-high-speed interconnection, ultra-efficient liquid cooling, and instantaneous burst power supply, achieving high system availability."
Overall, Huawei has introduced the Kunpeng series for general computing and the Ascend series for AI computing. In terms of architecture, Huawei has developed its self-designed Da Vinci architecture. On the software side, Huawei has launched the openEuler open-source OS along with supporting databases and middleware, covering the entire industry chain from hardware, architecture, frameworks, applications, to development and operation tools.
Cambricon possesses AI chip products including cloud-based AI chips and edge AI chips. Among them, the Siyuan 370 is Cambricon's third-generation cloud-based intelligent chip and the company's first AI chip to adopt Chiplet technology. Jingjiawei, a domestic GPU leader, offers AI chip products in the form of GPU chips.
Additionally, Moore Thread has comprehensively deployed in the GPU field. They have now released multiple GPU chips such as Suti and Chunxiao. Among them, Chunxiao is their second product, integrating 22 billion transistors and featuring the MUSA architecture general-purpose computing core along with tensor computing cores. It supports computational precisions including FP32, FP16, and INT8.
Currently, as international high-end AI chips face being 'pushed out,' domestic AI chips have undoubtedly become the best alternative. In recent years, under the influence of geopolitics, China's local AI chip industry has achieved certain developmental milestones, with some products even comparable to similar offerings from international companies.
However, it is important to note that hardware performance is just one aspect of AI chips. For domestic chips to be truly usable, software capabilities will be one of the more critical barriers. The release of computing power requires complex hardware and software coordination to transform the theoretical computing power of chips into effective computing power.
We observe that most of China's first-generation large model manufacturers currently use NVIDIA's A100 and A800 chips. This is not only due to NVIDIA's superior product performance but also because they have built a robust CUDA ecosystem.
CUDA is a GPU-based parallel computing platform and programming model introduced by NVIDIA, designed to accelerate large-scale data parallel computing. This enables GPUs to be utilized in a broader range of scientific and engineering computations. CUDA's robust ecosystem has attracted attention from numerous academic institutions and high-performance computing centers, providing NVIDIA with a strong competitive advantage in the market.
An analyst told Metaverse New Voice: "After years of development, NVIDIA's CUDA now boasts 4 million developers, effectively forming a monopolistic ecosystem barrier. Software ecosystems are precisely the most critical competitive factor for downstream customers." Switching ecosystems recklessly would mean increased learning costs, trial-and-error expenses, and debugging efforts for manufacturers.
However, in the face of CUDA's dominance, leading domestic AI chip manufacturers such as Hygon, Huawei, and Cambricon are continuously building their ecosystems based on their own products and solutions.
For example, Hygon's DCU product, the ShenSuan series, adopts a CUDA-compatible "CUDA-like" environment. Huawei's Ascend series uses its self-developed Da Vinci architecture, requiring large model manufacturers to pre-optimize hardware and software when using related chips. Although Cambricon's products include both cloud and edge chips, their ASIC architecture offers limited cost advantages for general-purpose computing.

Although there is still a considerable gap in ecosystem development between China's AI chip industry and CUDA, we have seen manufacturers taking action. Driven by complex international trade relations and geopolitical factors, 'domestic substitution' has become the main theme of China's semiconductor industry development.
Currently, chips have become one of the most promising fields in the semiconductor industry. AI chips, as the core market driving the development of the chip industry, have immeasurable industry value. With the gradual maturity of AI chip technology, their application scenarios are increasingly penetrating various smart terminal fields, playing an increasingly important role in China's technological development.
Metaverse New Voice has observed that in the current computing power field, traditional chip manufacturers represented by NVIDIA still dominate. However, tech giants like Microsoft, Amazon Web Services, and Google are also eyeing the 'lucrative' computing power chip market. Additionally, domestic chip manufacturers such as Huawei and Cambricon are continuously innovating and breaking barriers, emerging as new forces in the industry.
This has prompted the initial emergence of a 'Three Kingdoms' scenario in the entire AI chip industry. Moreover, as the AI era unfolds, this competition among the 'Three Kingdoms' will intensify further. Will it be the traditional chipmakers with first-mover advantages that continue to dominate, or will tech giants stage a comeback and 'counter-kill,' or perhaps domestic manufacturers achieve an overtaking maneuver?
It is foreseeable that every step forward in the AI chip industry will stir the nerves of the tech field. Who will emerge victorious in this 'Three Kingdoms' battle? The future is truly something to look forward to.
