OpenAI Developer Conference Stuns Again, Large Model Ecosystem Takes Shape
-
As expected, OpenAI's first developer conference delivered unexpected surprises.
Overnight, the large model community stepped into the world of Agents with one foot and waded into the ecosystem of GPT Store with the other.
On November 6, Eastern Time, the OpenAI Developer Conference officially kicked off. Founder and CEO Sam Altman took the stage for a 45-minute intensive presentation, once again demonstrating what it means to be "far ahead."
Let’s briefly recap the key highlights of the event, which essentially boiled down to three major announcements:
1. Technical Capabilities: GPT-4 Turbo introduced six major upgrades, including a 128K context length, enhanced control, updated knowledge, multimodal capabilities (voice and computer vision), model fine-tuning customization, and higher rate limits. Alongside performance improvements, API pricing was also reduced.

2. Replicable Capabilities: From GPT to GPTs, users can now create their own personalized GPT assistants. Enterprises can leverage OpenAI’s full suite of tools, "all tools," to build valuable internal solutions. Additionally, GPTs can evolve into Agents, paving the way for intelligent assistants.
3. Ecosystem Capabilities: Companies can not only develop GPTs but also list them on the GPT Store, sharing them with other users and earning revenue. This marks the beginning of an App Store-like commercial ecosystem.
As Zhou Feng, CEO of NetEase Youdao, noted, "The model updates primarily focus on performance and cost optimization. In terms of applications and ecosystems, OpenAI has introduced tools similar to LangChain (development toolchain) and LlamaIndex (data framework), ultimately aiming to realize the vision of AI Apps powered by Agents."
In short, OpenAI’s ecosystem capabilities address several critical challenges in large model development, setting the stage for a new wave of applications.
"Very exciting—there’s a lot of information to digest," remarked one attendee.
After the conference, discussions with leading large model entrepreneurs in China revealed widespread optimism. "OpenAI’s release of multimodal capabilities is a huge boon for developers, expanding the boundaries of what’s possible. I expect many new innovations to emerge," said Yang Zhilin, founder of Moon Dark Side, to Guangzhui Intelligence.
These 45 minutes added fuel to the second-stage ignition of the large model rocket.
Bringing Large Models to the Masses
"Identify demand, build ecosystems, find implementation." This succinct yet profound commentary came from a CEO of a leading Chinese AI company following OpenAI's first developer conference.
The market demand for ChatGPT is undeniably enormous. Sam Altman opened by sharing platform metrics: approximately 2 million developers currently build on OpenAI's API, over 92% of Fortune 500 companies use its products, and ChatGPT boasts ~100 million weekly active users.
While each iteration since GPT-3.5 has set new technical directions, the GPT-4 Turbo upgrade primarily focuses on refinement. Key improvements include:
- 128K context window (equivalent to 300+ book pages), 16× GPT-4's 8K limit, while maintaining accuracy
- Enhanced safety controls via new Json Mode for better API management and upcoming "Copyright Shield" legal protection
- Knowledge updates allowing document/database imports, with understanding current through April 2023
- Multimodal expansion opening DALL-E 3, TTS, and Whisper V3 APIs, marking a new phase beyond ChatGPT's initial speech/vision capabilities
A major price reduction accompanies these upgrades, addressing developer complaints about GPT-4's cost:
- GPT-4 Turbo: Input tokens 1/3 price, output tokens 50% cheaper
- GPT-3.5 Turbo: 4K version input tokens 1/3 price, 16K version input tokens 75% cheaper
As Altman noted, developer needs drive these changes, supported by technical and commercial considerations.
From a technical cost-saving perspective, foreign media reports suggest that OpenAI may transition from Stateless API to Stateful API. Sam Altman previously stated that with Stateful API, users no longer need to "pay repeatedly for the same historical conversations." Theoretically, this could reduce the cost of large model applications to one-twentieth of the original.
Commercially, OpenAI has been exploring monetization through APIs, ChatGPT personal and enterprise versions. However, competitors like Microsoft, Salesforce, and Meta are leveraging more cost-effective approaches, intensifying the pressure on OpenAI's commercialization efforts.
OpenAI's price reduction signifies that global large models have entered a new era of affordability and cost-effectiveness.
For startups and developers, this presents an opportunity for implementation, but it also poses challenges for companies like OpenAI in terms of technical capabilities, resource allocation, and computing power.
"After comprehensive consideration, we prioritized price, but speed remains a challenge. This will be a key focus of our future research," said Altman.
Several developers using GPT-4 tools reported that its rate limits have already doubled.
"Computing power shouldn't be an issue; OpenAI has ample reserves," commented Yang Zhilin.
Providing 'Dream-Building' Tools for Entrepreneurs
In discussions with large model entrepreneurs, Guangzhui Intelligence found that many are hindered not by a lack of ideas but by technical challenges like data, computing power, tools, deployment, training, and inference.
For example, a developer of a large model-based puzzle game on Zhihu had to shut down the game due to unexpected user demand overwhelming their computing resources, leaving players disappointed.
Similarly, domestic entrepreneurs recognize Agent as a future direction but face overwhelming hurdles. One Agent startup founder shared, "Data cleaning, long-text memory, coding, testing, deployment, costs—it's 81 challenges, each a potential dead end for startups."
Globally, Agent technology is far from widespread adoption, with Code Agent being the most viable current application due to its alignment with model training and task execution.
Now, OpenAI's release of the all tools and Assistant API promises to resolve these issues effectively.
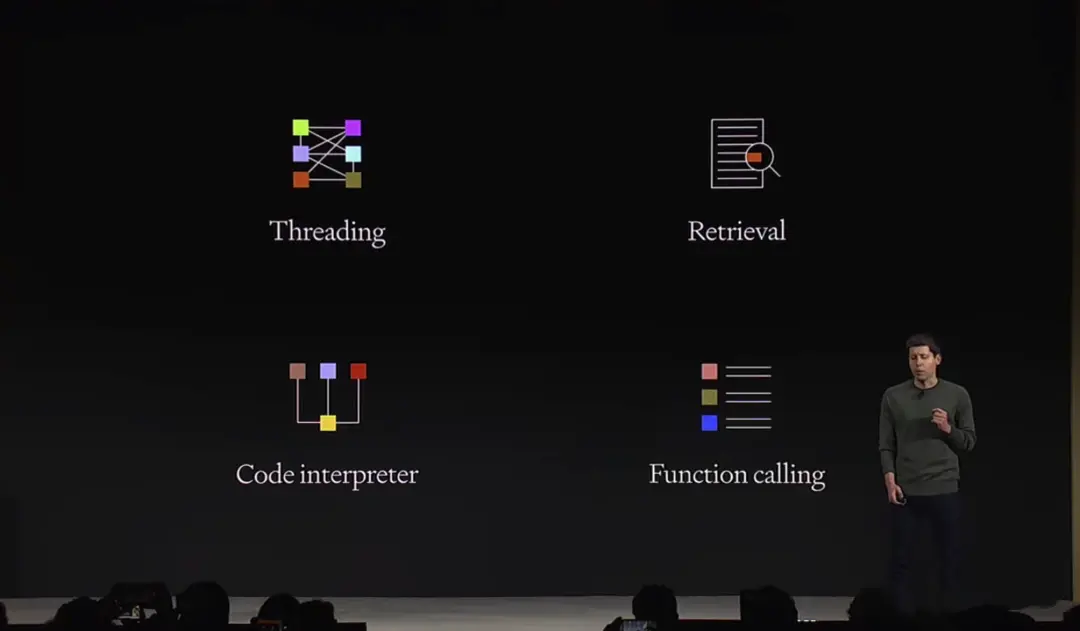
The Assistant API is a tool specifically designed for AI Agent developers, encompassing features such as long threading, retrieval, code interpreter, and function calling.
- Persistent and infinitely long threads allow developers to offload thread state management to OpenAI, overcoming context window constraints.
- Retrieval functionality leverages external knowledge to enhance the model, such as proprietary domain data, product information, or user-provided documents.
- Code interpreter enables writing and executing Python code in a sandbox environment, generating graphs and charts, and processing files with various data formats, similar to ChatGPT Plus.
- Function calling has been updated to allow multiple functions to be called simultaneously, with responses merged into the message output.
In summary, these new features precisely target developers' pain points, lowering the barrier to entry, shortening development and testing cycles, and reducing labor costs when working within OpenAI's comprehensive toolchain.
"We have a love-hate relationship with OpenAI. On one hand, its upgraded tools can instantly streamline our operations, but on the other, we must remain vigilant about being replaced by OpenAI," said an Agent entrepreneur.
The spotlight of this release is the "Agent." Sam Altman defines an Agent as a personalized and customized extension of individuals, leveraging tools and AI to accomplish tasks on their behalf. Users only need to specify their needs, and the Agent will handle the rest.
Analysis by Guangzhui Intelligence reveals that Agents are not standalone; they are built upon GPT's large model foundation, first giving rise to "GPTs" as extensions of GPT, and then evolving into "AI Agents."
"At OpenAI, we firmly believe that gradual, iterative deployment is the best approach to addressing safety challenges in AI. We consider it crucial to proceed cautiously with future Agents, requiring extensive technical work and societal deliberation. That’s why we’re taking this small step toward the future—GPTs," Altman stated.
OpenAI's path to future Agents is taking shape. As they put it, "This is just the first step toward AI Agents." The future may involve multimodal and multi-agent systems.
Building the Foundation of the Large Model Ecosystem
The iteration of technology is undoubtedly exciting, and the introduction of tools has made developers' work more convenient and efficient. However, what's more significant is that OpenAI, on its own, has further advanced the commercialization of large models.
Back in May, when OpenAI opened its plugin system, the first batch included 70 applications related to large models, such as word-guessing games, translation tools, and stock data lookup. At that time, it was predicted that an 'App Store for large models' had arrived. However, while the number of applications gradually increased, no 'blockbuster' app emerged.
Some investors believe that the current GPT Store is similar to mini-programs when they first appeared—gradually building up capabilities. This upgrade symbolizes a step toward maturity, and the next WeChat or TikTok could very well emerge from here.
During this launch event, OpenAI restructured the application store's system, made minor adjustments to the page layout, placed ChatGPT on the same level as third-party applications, and expanded the development scope to a whole new dimension. According to Altman, each GPT is like a custom version of ChatGPT tailored for a specific purpose.
What's even more exciting is that, similar to Apple's App Store, users can search and download GPT applications in the GPT Store. The store will also recommend high-quality products in categories like productivity, education, and entertainment. OpenAI has also clarified that creators can earn revenue based on the usage of their GPTs. This means that applications based on large models now have a 'container,' and developers have found a 'marketplace' for buying and selling.
To give a simple analogy: large models are like plots of land, tools are like hammers and nails, and different developers will build different houses. The GPT Store is a real estate market where the houses built can not only be used by the builders but also rented or sold.
With a 'trading ground' for commercialization, entrepreneurs now have positive feedback, making entrepreneurship no longer just about passion and dreams but also about the possibility of real earnings.
This might be what large model entrepreneurs refer to as 'finding a landing.' In the first half of the year, AI entrepreneurship was all about 'burning money.' A funding round of 50 million was just a drop in the bucket for large model startups. Investors were hesitant, and entrepreneurs couldn't come up with new stories.
At the event, OpenAI staff demonstrated the use of a travel GPT they built: it not only lists travel suggestions for Paris but also marks the locations mentioned in the plan on a map by category. This could easily be monetized through user fees or a membership model.
While this doesn't mean every application on the GPT Store will make money, it at least provides a window to gain the first batch of seed users, which can then feed back into product improvement and create a growth flywheel.
Looking back at the era of mobile internet applications, entrepreneurs in every niche market could uncover countless needs to create new apps, which was precisely what excited them. It was then that the button was pressed to start redoing all apps from scratch.
"We believe AI will empower individuals and organizations with new capabilities on an unprecedented scale. This will elevate all of humanity to a level we have never seen before," Altman remarked in conclusion.
Clearly, OpenAI aims to achieve much more. The foundational infrastructure is now in place, and all that remains is time and the contributions of other players in the ecosystem to bring it to fruition.
