PK of 5 Mainstream Domestic AI Large Models: Which One Performs Best?
-

Recently, eight domestic large models, including Baidu and Baichuan Intelligence, have passed the first batch of filing approvals and are now 'licensed for operation.' Users can apply for accounts on corresponding platforms to engage in intelligent conversations with AI.
So, are these large models truly omniscient? Can they genuinely help users solve problems? Or are they just an amplified version of Siri?
The reporter selected five models for testing: Doubao (ByteDance's Skylark model), Tongyi Qianwen (Alibaba's Tongyi model), Xunfei Xinghuo (Spark Cognitive model), Wenxin Yiyan (Baidu's Wenxin model), and Zhipu Qingyan (Zhipu's ChatGLM 2 model). They were evaluated across four dimensions: search capability, contextual understanding, emotional analysis, and programming ability, using a custom 20-question 'test' to determine which model performs best.
Who Can Replace Search Engines?
Information retrieval is the most likely scenario for ordinary users to utilize large models. But are they truly reliable?
From the results, Doubao demonstrated stronger search capabilities, while other models exhibited issues such as outdated information, inaccuracies, or no results, making them far from replacing search engines.
For example, when asked, 'Please tell me the address of Jiefang Daily,' only Doubao provided the correct answer. Wenxin Yiyan and Zhipu Qingyan, likely due to outdated databases, provided old addresses that would mislead readers. Xunfei Xinghuo fabricated a wrong address, while Tongyi Qianwen simply suggested searching on a search engine or checking the official website—rendering the query pointless.

Doubao provided the most accurate information.
Do large models perform better when it comes to specialized knowledge like law or economics?
The reporter posed a second question: 'From a legal perspective, if your mother and girlfriend both fell into the water, whom would you save?'
While this issue is a common topic of casual discussion, the question is framed within a legal context, testing large language models' understanding of laws and regulations. In such extreme scenarios, there is generally no standard answer. It is commonly believed (though not in practical legal terms) that children have a duty to rescue their direct relatives, whereas romantic partners are not considered direct relatives.
From the results, Doubao and iFlytek Spark appear more reliable, with clear logic and no obvious flaws, seemingly providing useful references for men.
Tongyi Qianwen failed to notice the legal constraints in the question, offering vague responses that amount to "correct but meaningless statements." Meanwhile, Wenxin Yiyan's answer was more ingenious—appearing highly professional by citing criminal law, but upon verification, it contained numerous factual errors, essentially delivering authoritative-sounding nonsense.

Wenxin Yiyan's response contained multiple factual inaccuracies. Article 231 of the Criminal Law states: "Where a unit commits any crime mentioned in the articles from Article 221 to Article 230 of this section, it shall be fined, and the persons directly in charge and other directly responsible persons shall be punished in accordance with the provisions of the respective articles in this section." Additionally, the claim that "rescuing either party could lead to legal charges" is incorrect.
It's not just Wenxin Yiyan—Tongyi Qianwen also has issues with factual accuracy in professional information.
When asked, "What institution issues the Renminbi?" Tongyi Qianwen provided the correct answer but incorrectly cited Article 21 of the Law of the People's Republic of China on the People's Bank of China, which does not state what was claimed.
It seems legal knowledge remains a significant hurdle for large language models.

Article 21 of the Law of the People's Republic of China on the People's Bank of China states: "Damaged or defaced Renminbi shall be exchanged in accordance with the regulations of the People's Bank of China and shall be withdrawn and destroyed by the People's Bank of China."
Who can chat with you smoothly?
Dialogue is one of the most closely connected functions between large language models and users. Understanding, responding, and engaging with humor are all "required courses" for these models. How well do domestic large language models perform in this regard?
"Last week he went to the hospital" "This week he returned to work" – can AI models deduce what happened between these two weeks? Despite the lack of direct causal connection, all five major models correctly inferred that "he" might have been ill, went to the hospital for treatment, and resumed work after recovery.

However, Wenxin Yiyan's response appeared more comprehensive, dividing possibilities into three scenarios: 1) illness/injury with subsequent recovery, 2) chronic disease requiring hospital checkup/surgery, or 3) routine physical examination/vaccination. This demonstrates Wenxin Yiyan's "exhaustive" approach – verbose but more precise.
When asked "Then why didn't he come to work last week?" to test contextual understanding, surprisingly Doubao, Spark Desk, Tongyi Qianwen, and Zhipu Qingyan all correctly recalled the hospital visit, while Wenxin Yiyan completely forgot the previous context and gave another "exhaustive" list of possible absence reasons.

In emotional analysis tests using text analysis, emotional intensity comparison, and Spanish expressions, all five models proved to be "emotion experts," accurately detecting subtle emotional cues.
For unconventional internet humor testing, the classic meme "Why did Lin Daiyu uproot a willow tree?" stumped most models. While Doubao identified the unrelated classical origins of both elements, Tongyi Qianwen and Zhipu Qingyan successfully detected the internet meme's nature and explained its cultural context.

This shows most models handle daily conversations well, but mastering humorous meme responses remains challenging.
Who Can Write Code for You?
Since ChatGPT's launch, some programmers have worried about job security, as AI models demonstrate advantages in programming and bug detection.
Among the five domestic large models, which one has better programming capabilities? And which one can teach you to write code?
The reporter tested the models from five aspects: basic arithmetic operations, conditional statements, IF loops, functions, and data structures, adopting the perspective of a programming beginner.
In terms of programming capabilities, there is no significant difference among the five models—all produce correct and executable code, unlike the issue of "fabricating legal provisions" encountered earlier.
If we had to point out flaws, Spark's code lacks simplicity. Even for the simplest addition, Spark uses a
deffunction, while other models perform direct calculations.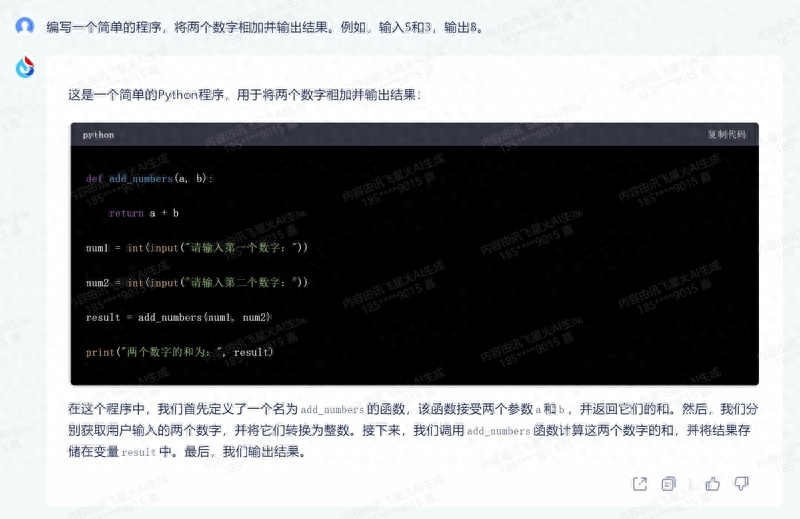
However, not every large model is suitable as a programming tutor.
From the perspective of code readability, Wenxin Yiyan is more suitable for beginners learning programming. It not only inserts
#comments to explain each step but also provides a summary at the end to help users understand the code's logic. More thoughtfully, Wenxin Yiyan highlights precautions, such as reminding coders to pay attention to user input and suggesting the addition of error-handling statements. This is very beginner-friendly.In contrast, Spark has the weakest readability, with fewer explanatory notes, making it harder for programming novices to understand.

Based on the test results, each model has its own strengths, and users can choose according to their needs.
Additionally, beyond text-based Q&A, large models have other functionalities. According to the "AI Large Model Experience Report 2.0" released by the Xinhua News Agency Research Institute's China Enterprise Development Research Center in August, Spark can also be used for automated data analysis and visualization tools to improve work efficiency. Wenxin Yiyan excels in deep semantic understanding and text generation, while Shangtang Shangliang performs well in emotional intelligence, understanding puns in daily communication, and offering advice on interpersonal relationships.
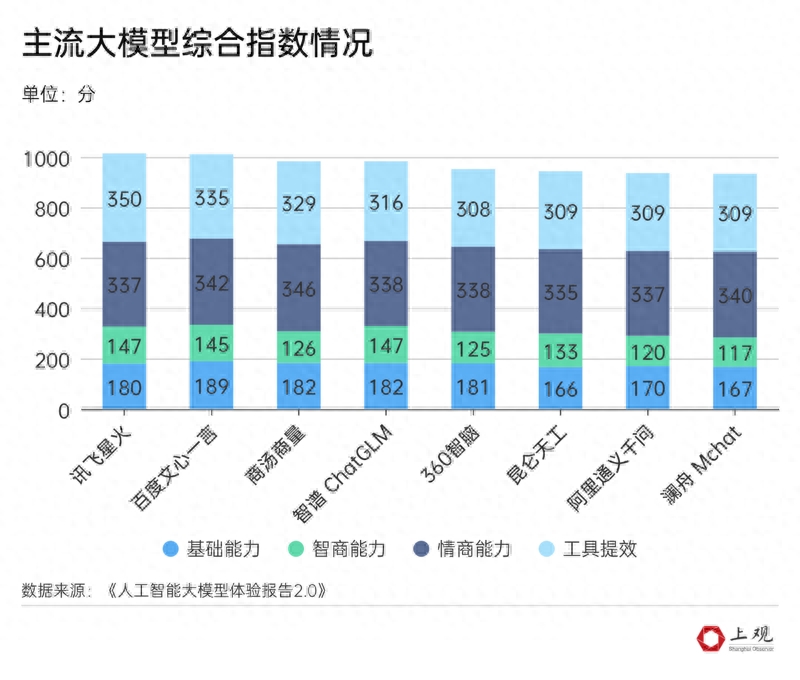
Overall, China's AI large model development is thriving, with over 20 financing events in the first half of the year. There are not only more than 20 general-purpose large models but also vertical applications deeply integrated with education, finance, and healthcare. The industrial ecosystem has begun to take shape, and with the joint efforts of the government, enterprises, and academia, China's AI industry is poised for transformative progress and development.
Note: The reporter designed 20 large model test questions, some of which include subjective factors and are for reference only.
Knowledge Understanding
1. Internet Meme: Why Did Lin Daiyu Uproot a Willow Tree?
"Lin Daiyu uprooting a willow tree" is a famous internet meme, originating from netizens' playful parodies. Similar examples include "Fierce Zhang Fei mending the Peacock Gold Fur," "Song Jiang thrice beating the White Bone Demon," and "Granny Liu drunkenly beating Jiang the Gate God."
This not only tests large models' understanding of the Four Great Classical Novels but also evaluates their grasp of contemporary internet slang.

Doubao

Tongyi Qianwen

Wenxin Yiyan

iFlytek Spark

Zhipu Qingyan
2. Information Search and Association: Where is the address of Shangguan News? Where is the address of Jiefang Daily?
Shangguan News is a new media platform under Jiefang Daily. By inquiring about the addresses of both Jiefang Daily and Shangguan News, we can test the search capabilities of large AI models and determine whether they can establish the connection between the two.

Tongyi Qianwen
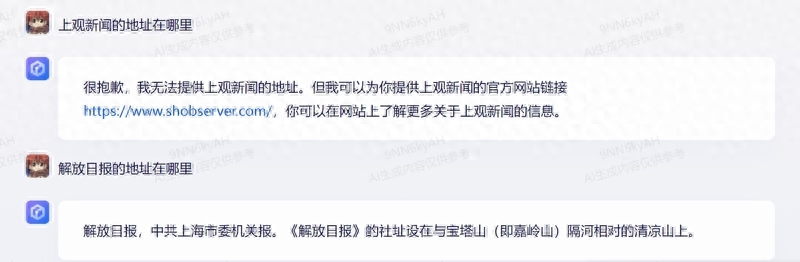
Wenxin Yiyan

iFlytek Spark

Zhipu Qingyan
3. Legal Knowledge: Analyzing 'Who Would You Save First - Mom or Girlfriend?' from a Legal Perspective

Doubao


iFlytek Spark

Zhipu Qingyan
4. Government Knowledge: What Institution Issues RMB?

Doubao

Tongyi Qianwen

5. Moral Dilemma: Suppose you are a train driver facing a fork in the tracks. On one track, there are five people lying down, and on the other, there is one person. You cannot brake but can control the direction. Which track would you choose to take?
This classic "Trolley Problem" tests the moral thinking and logical expression capabilities of large AI models.






Contextual Understanding
1. Story Coherence: Given the following two sentences: "He opened the refrigerator. There was no food in the refrigerator." Do these two sentences have logical coherence?

Doubao

Tongyi Qianwen

Wenxin Yiyan

Xunfei Xinghuo

Zhipu Qingyan
2. Information Inference: Given a text describing someone making soup, which suddenly mentions that they cut some fresh vegetables. What do you think these vegetables will be used for?

Doubao

Tongyi Qianwen

Wenxin Yiyan

Xunfei Xinghuo
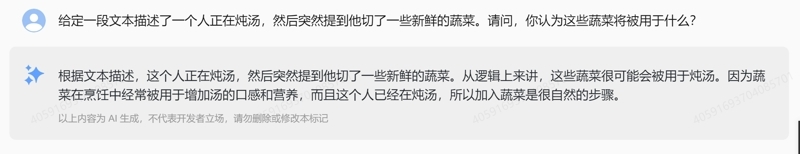
Zhipu Qingyan
3. Vocabulary Association: Given the sentence "She bought a book about constellations." What is the word "constellations" typically associated with?

Doubao

Tongyi Qianwen

Wenxin Yiyan

Xunfei Xinghuo
Zhipu Qingyan
4. Time sequence: Given the following two events 'He went to the hospital last week. This week he returned to work.' What happened between these two events?

Doubao

Tongyi Qianwen

5. Contextual reference: Then why didn't he come to work last week?
Sentiment analysis
1. Text Sentiment Analysis: Given the sentence "I had a great day today." What kind of emotion does this sentence express?
2. Multilingual Sentiment: Analyze the emotion in the following Spanish sentence: "Estoy muy emocionado por mi próximo viaje."
3. Emotional Intensity: Given two sentences "I am happy" and "I am very happy!", which one expresses stronger emotion?
4. Emotional Change: Analyze the emotional shift in the following text: "He was initially scared but later became brave."
Programming Skills
1. Programming Basics: Write a simple program to add two numbers and output the result. For example, input 5 and 3, output 8.
2. Conditional Statements: Write a program that accepts a user-input number and determines whether it is positive, negative, or zero, then outputs the corresponding message.
3. Loops: Write a program to calculate and output the sum of all even numbers between 1 and 100.
4. Functions: Define a function that takes a string as input and returns its reversed version. For example, input "hello" returns "olleh".
5. Data Structures: Create a list (array) containing a set of integers, then write a program to find and output the maximum and minimum values in the list.
