$30 Billion: Amazon Makes Largest Investment in AI Sector to Date
-
The overnight success of ChatGPT has sparked an industry-wide pursuit of large AI models and signaled the beginning of the 'Hundred-Model War.' To compete with OpenAI's ChatGPT, major players are placing their bets. E-commerce giant Amazon has recently ramped up its efforts in AI, investing $4 billion (approximately 29.23 billion RMB) in Anthropic, OpenAI's top rival. This marks Amazon's largest investment in generative AI so far.
Shortly after Amazon announced this investment, Anthropic reportedly sought additional funding. On October 4, news emerged that Anthropic was in talks with Google and other investors to raise another $2 billion (approximately 14.62 billion RMB), potentially valuing the company at $20-30 billion post-investment. This new valuation would be more than five times its $4 billion valuation in March, making this less-than-two-year-old AI startup the talk of the industry.
What makes Anthropic so appealing to Google and Amazon? A look at the September rankings from SuperCLUE, a comprehensive benchmark for Chinese general-purpose large models, provides some insight. Test results show that Anthropic's Claude 2 ranks third overall, trailing only OpenAI's GPT-4 and GPT-3.5.
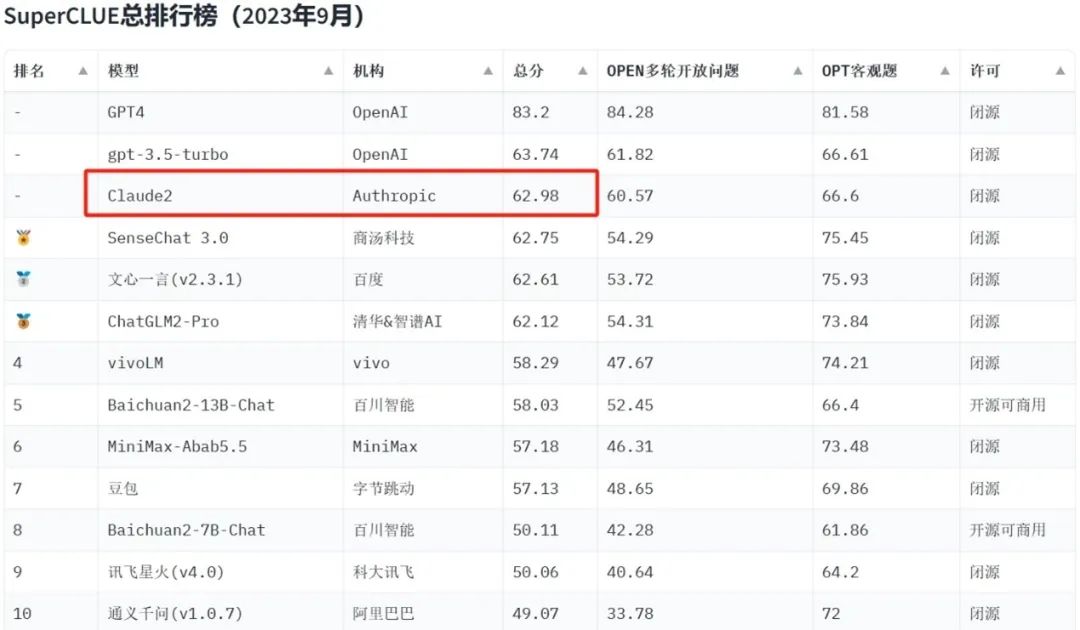
Beyond its strong community rankings, Anthropic boasts an exceptional founding team. Siblings Dario Amodei (former OpenAI VP of Research) and Daniela Amodei (former VP of Safety Policy) led the 2021 founding, joined by core researchers like Jared Kaplan and Tom Brown who contributed to GPT-2/GPT-3 development.
Responding to ChatGPT's launch, Anthropic released Claude within two months and upgraded to Claude 2 by July. Benchmarks show Claude 2 matches GPT-3.5 overall but trails GPT-4, excelling in document processing (100K token context vs. GPT-4's 32K) while lagging in coding. Its 3x larger context window enables analysis of entire books.
Anthropic pioneers Constitutional AI - establishing governing principles for models, contrasting with OpenAI's RLHF approach. This framework aims to automate AI alignment and prevent superintelligent risks, forming their core commercial differentiation.
With large models being capital-intensive, Anthropic seeks $5B funding for Claude-Next (projected 10x more powerful than current AI). Amazon's $4B investment will fuel this development targeting a dozen industries. Revenue is expected to double to $200M in 2023 and reach $500M by 2024 - potentially outpacing OpenAI's monetization.
Across the industry, Anthropic has emerged as one of Silicon Valley's most sought-after AI companies by investors, with an overall valuation close to $5 billion, ranking second only to OpenAI.
Each leap in AI model capabilities exponentially increases the demand for computing power. This inevitably triggers fierce competition for underlying computing infrastructure and massive funding, making it a brutal battle among tech giants. In this AI wave, U.S. tech giants are leveraging their strengths, shifting from pure model competition to core capabilities combining models and computing power. For Amazon, Microsoft, and Google—the three global cloud service leaders—this presents a new test of their cloud computing and service capabilities. Meanwhile, emerging players like Tesla are also eager to join the fray. The focus of competition has now shifted to attracting developers and users, securing capital, and building ecosystems.
From AI model iteration to computing power consumption, capital investment, attracting developers and users, forming an AI cloud service ecosystem, and ultimately reaping commercial returns—this is the virtuous cycle tech giants hope to achieve. In the internet era, Amazon led in cloud services, but in the AI era, its lag in AI models and computing power has allowed Microsoft and Google to erode its market share. Microsoft's partnership with OpenAI and Google's with DeepMind have given Azure and Google Cloud an edge over AWS, not only in AI value-add but also in stable business outlets. This is a key reason Amazon is heavily investing in Anthropic.
Microsoft: After investing in OpenAI in 2019, Microsoft added another $10 billion in early 2023, securing a 49% stake. Riding the ChatGPT wave, Microsoft transformed from a software provider to a cloud service leader and now an AI frontrunner. It aims to replicate this success by strategically investing in other AI startups like Inflection AI and Adept. Microsoft also collaborates with Meta's open-source LLaMA 2, betting on both open and closed AI models to boost Azure's competitiveness.
Google: Despite merging DeepMind and Google Brain, Google continues investing in Anthropic. OpenAI's rise has pressured Google, leading to a $400 million investment in Anthropic for a 10% stake in February. Reports suggest Anthropic is negotiating another $2 billion funding round with Google and others. Additionally, after launching Bard, Google unveiled Gemini, touted as GPT-4's strongest challenger, though its performance remains unproven.
Amazon: A latecomer in AI, Amazon missed the opportunity to partner with OpenAI five years ago, allowing Microsoft to become the pioneer in this AI era. In its investment in Anthropic, Amazon was about six months behind Google, making an initial $1.25 billion investment in late September this year, with potential follow-on investments up to $4 billion. Currently, Amazon holds a minority stake in Anthropic, whose valuation remains undetermined. If completed, this would be Amazon's largest investment in the AI field.
Meta: Another latecomer in AI, Meta has shifted its focus from the metaverse to AI, announcing the first version of its large language model, LLaMA. To catch up, Meta has adopted an 'open-source and free' strategy. Unlike Microsoft and Google, which use AI to enhance existing products (e.g., Microsoft integrating OpenAI into Bing, Office, and Azure; Google applying AI to search, Workspace, and Maps), Meta aims to leverage AI to build a more futuristic metaverse, showcasing its ambitious vision.
Tesla/xAI: Elon Musk, a co-founder of OpenAI who has since left, established xAI with the goal of understanding the true nature of the universe and creating a 'good artificial general intelligence (AGI).' On August 28, 2023, Tesla deployed a supercomputer cluster comprising 10,000 Nvidia H100 GPUs to train its Full Self-Driving (FSD) system and other AI applications. Additionally, Tesla's Dojo supercomputer began mass production in July 2023, further strengthening its computing infrastructure. The Dojo's core is Tesla's self-developed D1 chip, built on TSMC's 7nm process and advanced packaging technology. In 2023, Tesla allocated about 5,000 12-inch wafers to TSMC, with plans to double that to 10,000 in 2024. In the future, Tesla may open Dojo to external users, similar to Amazon's AWS cloud services.
Apple: With its vast Siri user base, Apple appears somewhat dismissive of the ChatGPT trend, often avoiding the term 'AI' in public statements in favor of 'machine learning.' Overall, Apple's AI efforts are focused on optimizing existing product features. However, CEO Tim Cook recently stated, 'AI is virtually everywhere in our products, and we have a lot of work going on in generative AI research.'
Looking specifically at Amazon, its business focus originally came from AWS's cloud computing division. In Q2 this year, AWS revenue grew by 12.16% to $22.14 billion, but profits fell by 6.12% to $5.365 billion, with operating margins dropping 4.72 percentage points to 24.23%. Although AWS's revenue contribution isn't exceptionally high, its profit contribution still accounts for the majority. Clearly, as a globally renowned cloud service provider, Amazon's cloud computing profits barely compensate for the meager profits or even losses in its retail business.
However, with OpenAI's deep integration with Microsoft boosting Azure's market share, Amazon faces significant threats. During a recent earnings call, CEO Andy Jassy noted that cloud computing margins have declined sharply in recent quarters, suggesting diminishing returns to scale. Yet AWS remains the undisputed leader in cloud infrastructure, maintaining advantages in customer base, partner ecosystem, and feature breadth while delivering the strongest operational performance. While generative AI has sparked tremendous interest, most discussions focus on the application layer, particularly OpenAI's ChatGPT. Amazon's strengths in foundational infrastructure could become a new growth area.
Generally, enterprises wanting to develop large AI models face costs of billions of dollars and years of training, requiring substantial funding and equipment. A more cost-effective solution is fine-tuning powerful open-source base models to meet diverse business needs. It's predicted that by 2026, the enterprise AI market will grow from $43 billion in 2023 to $98 billion (approximately ¥716.85 billion), representing massive potential.
In response, Amazon AWS launched the fully managed foundation model service "Amazon Bedrock" in April, positioning itself as a "critical infrastructure provider" in the AI model competition to reclaim market share from Microsoft and Google Cloud. Additionally, Amazon's investment in Anthropic includes Anthropic's commitment to using AWS's custom AI chips (Trainium and Inferentia) to build, train, and deploy future AI models. AWS and Anthropic plan to collaborate on these technologies.
Anthropic has also committed to providing AWS customers with access to its future AI models via Bedrock. Compared to other one-stop AI platforms, Amazon Bedrock's advantage lies in seamless integration with AWS services, easier access to data stored in Amazon S3, and benefits from AWS's access control and governance policies. The service's key value is enabling users to build generative AI applications by combining existing models, dedicated AI computing power, tools, and their own data.
It can be said that generative AI has reshaped the competitive landscape of cloud computing services, making capabilities at the model, framework, and application levels more critical while also promoting the emergence of new business models like 'Model-as-a-Service.' For instance, Amazon's Bedrock platform has turned large models into directly usable services, facilitating easy access and application of generative AI across industries. Tang Zhenyi, Vice President of SenseTime, told Rongzhong Finance that in the future, enterprises might not need to develop and train large models themselves. By leveraging foundational general-purpose models and combining them with industry-specific data, they can cultivate diverse 'towering trees' of applications.
Currently, China's large AI models are accelerating their development—Baidu's 'ERNIE Bot,' Tencent's 'Hunyuan,' and iFlytek's 'Spark' are notable examples. Data shows that at least 130 domestic companies are researching large model products, with 78 focusing on general-purpose models.
As the battle for large models intensifies, for Amazon, investing in Anthropic is no longer optional but a necessary strategic move to compete effectively. For major investors like Google, Microsoft, Amazon, and Nvidia, paying high premiums for trending AI startups not only reflects confidence in their technological potential and market prospects but also presents opportunities to expand their own businesses—whether through increased cloud server usage or adoption of proprietary chips—creating a win-win scenario.
