McKinsey Releases Generative AI Report: Human-Level AI Expected by 2030
-
McKinsey's groundbreaking report has been released!
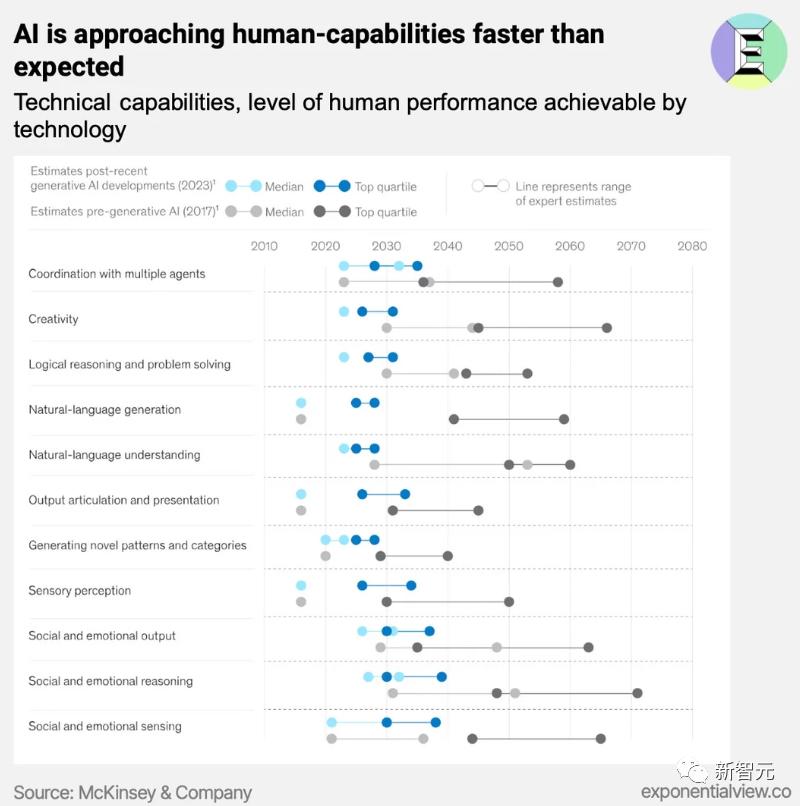
The core conclusion can be summed up in one sentence: AI will reach human-level capabilities faster than imagined, with a median prediction pointing to achievement before 2030.
Notably, compared to predictions made in 2017, this new report reflects significantly more optimism.
The image above shows the final results chart from the report, which we will analyze in detail later.
The report begins with a perfect summary of how technology currently impacts our lives.
In short, AI has already permeated every aspect of our daily existence.
In 2016, when DeepMind's AlphaGo defeated world champion Lee Sedol, AI briefly captured global attention. However, as it was confined to the game of Go, the hype gradually faded.
But this year is different.
Beyond ChatGPT's astronomical user growth, generative AI products like Copilot and Stable Diffusion have swept through our lives like a storm.
The key difference now is that these AI tools are universally accessible. Everyone can use ChatGPT for writing, Midjourney for image creation, or Copilot for making presentations.
ChatGPT powered by GPT-4 shows dramatic performance leaps from GPT-3.5. Meanwhile, Anthropic's Claude can process 100,000 tokens per minute (equivalent to a novel's length), a tenfold improvement over its March 2023 version.
The report focuses on AI's unprecedented development speed, with breakthroughs occurring within months.
Here, generative AI is defined as applications built on foundation models. These models have expanded capabilities in images, video, audio, and code, with significant performance enhancements across existing functions.
The report notes that our understanding of generative AI's full potential remains in its infancy.
This is why McKinsey produced a report—to gain a more thorough understanding of the future of generative AI.
Currently, major enterprises are experimenting with generative AI applications, rapidly adapting workflows to accommodate technological advancements.
The report emphasizes the necessity to fully comprehend how generative AI will impact our society and economic development.
The following diagram illustrates how the report employs two complementary perspectives to identify which fields can derive the greatest value from current generative AI capabilities and quantify that potential.
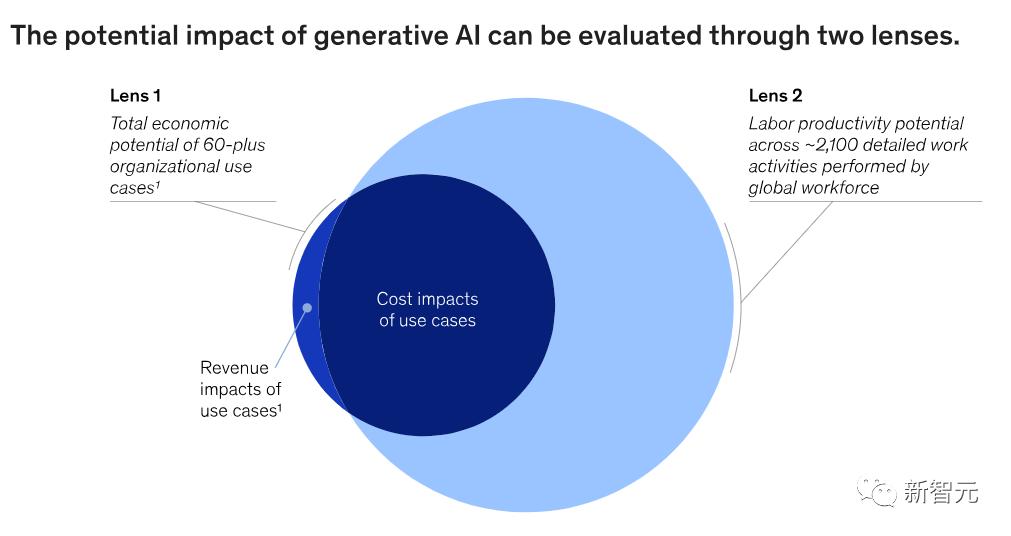
Lens 1 in the diagram represents a comprehensive scan of enterprises capable of utilizing generative AI, referred to as 'use cases'.
For example, one marketing use case involves applying generative AI to create personalized emails and similar content. The measurable outcomes include reduced costs for producing such content and increased revenue through the enhanced effectiveness of high-quality content at scale.
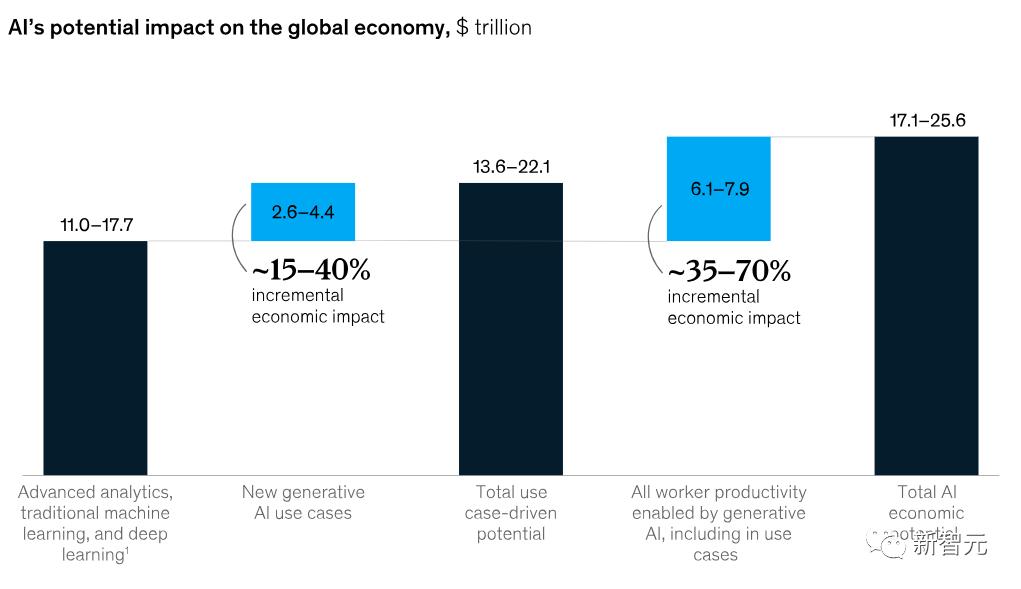
Accordingly, the report identifies a total of 63 generative AI use cases spanning 16 business functions. When applied across industries, these could deliver annual economic benefits ranging from $2.6 trillion to $4.4 trillion.
This represents a significant increase - 15% to 40% growth - compared to the previously estimated $11-$17.7 trillion economic value predicted by McKinsey in 2017.
Lens 2 complements Lens 1 by analyzing generative AI's potential impact on approximately 850 occupations. Experts simulated various scenarios to estimate when generative AI could perform each of the 2,100+ tasks that constitute the global economy - including activities like communicating operational plans with colleagues.
This approach allows estimation of how generative AI, with current capabilities, could affect labor productivity across all current global workforce activities. Some impacts overlap with the cost reductions mentioned in Lens 1, leading the report to assume that cost reductions result from productivity improvements.
Excluding such overlaps, the total economic impact of generative AI reaches an annual range of $6.1 to $7.9 trillion, as shown in the figure below.
While the current economic benefits are already substantial, the report indicates that this is just the beginning.
Now, let's discuss its potential.
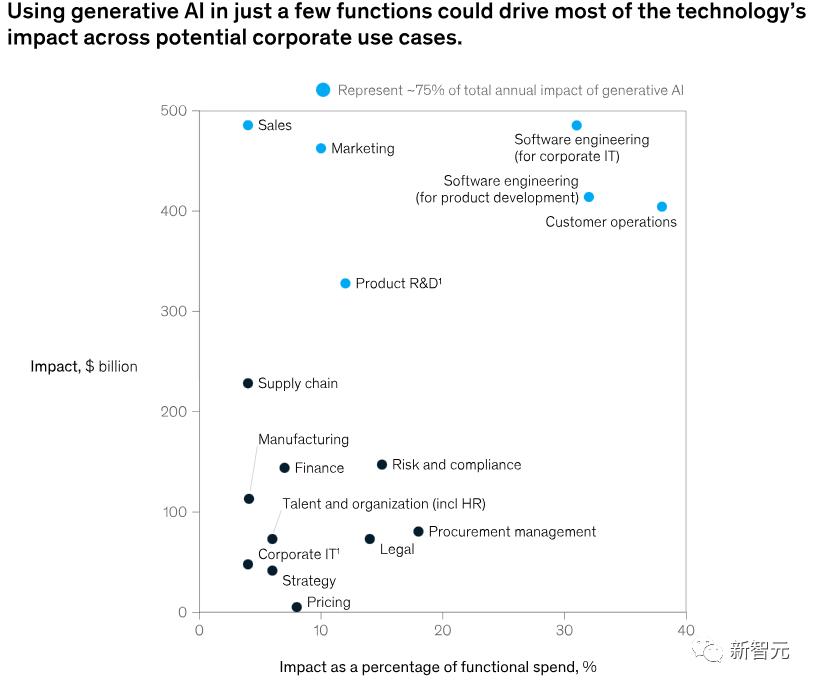
Generative AI could impact most business functions. However, when measured by the proportion of technological influence on functional costs, a few key functions stand out, as illustrated below.
McKinsey's analysis of 16 business functions revealed that just four—customer operations, marketing and sales, software engineering, and R&D—account for approximately 75% of the total annual value from generative AI use cases.
In simple terms, not all business functions benefit equally from AI when viewed from a technical perspective.
The report indicates that in previous evaluations of AI applications, generative AI demonstrated substantially lower potential value in certain work domains, including manufacturing and supply chains.
The primary reason lies in the inherent nature of generative AI itself.
Beyond specific use cases where generative AI can deliver potential value, it also holds the capability to revolutionize corporate knowledge management systems, thereby creating value across entire organizations.
As we know, generative AI possesses strong natural language processing capabilities, enabling employees to more conveniently query and retrieve internally stored company knowledge.
This clearly enhances teams' ability to quickly access relevant information, allowing them to make more informed decisions rapidly and develop effective strategies.
Before the advent of generative AI, similar tasks might have taken workers an entire day to complete. With generative AI taking on these responsibilities, it undoubtedly generates significant efficiency gains.
Additionally, generative AI can enhance value by collaborating with workers, accelerating their efficiency, and augmenting their capabilities.
(Note: The playful remark about 'whose DNA is activated' and the editor using AI to generate the article has been omitted as per translation guidelines.)
Among the 63 use cases analyzed in the report, generative AI has the potential to create a total value of $2.6 trillion to $4.4 trillion across various industries.
Of course, the actual impact depends on multiple factors, such as the combination of different functions, their respective importance, and—more critically—the revenue scale of the industries themselves, as illustrated in the figures below.
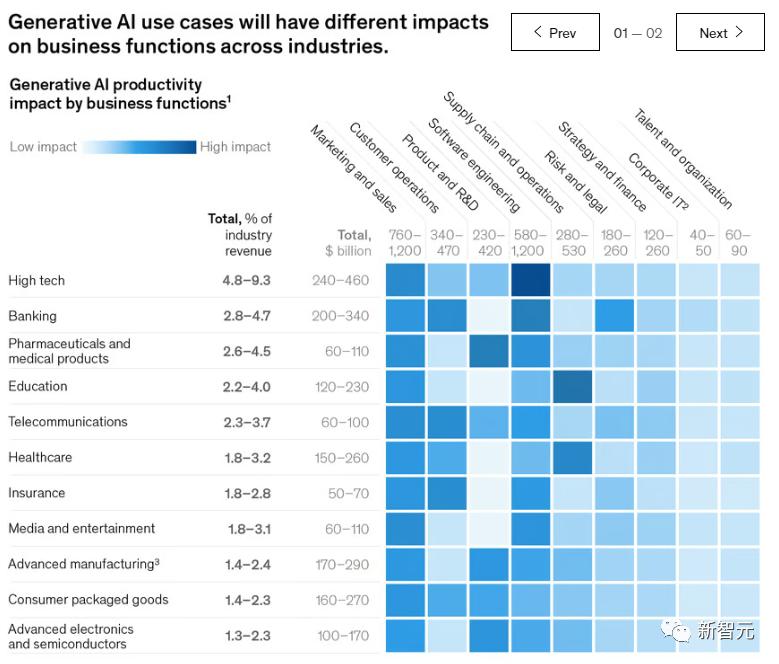
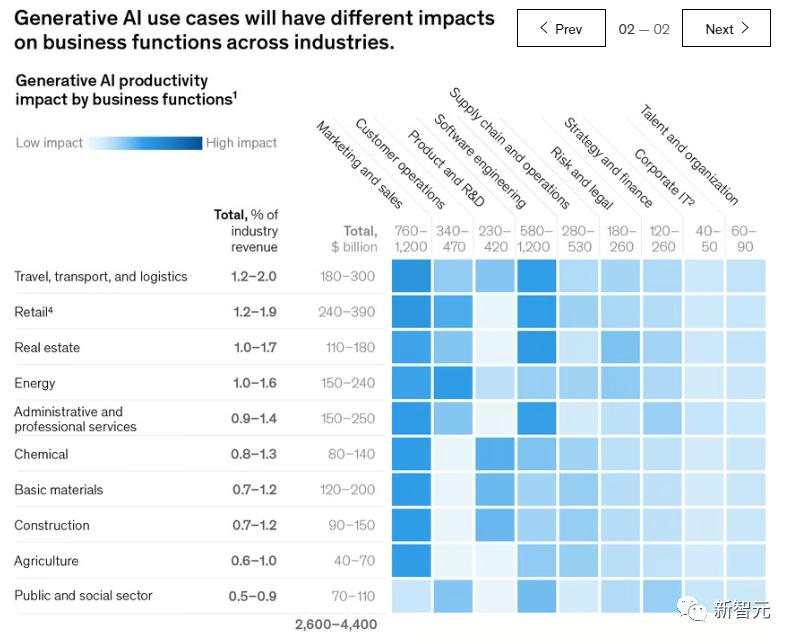
For example, according to the report, generative AI could generate approximately $310 billion in additional value for the retail industry (including automotive dealers) by improving functions such as marketing and customer operations.
In contrast, most of the potential value in the high-tech sector stems from generative AI's ability to improve the speed and efficiency of software development, as illustrated in the figure below.

The report estimates that this figure will become increasingly impressive in the future—given AI's rapid advancements.
Since 2017, the McKinsey Global Institute has been analyzing the impact of technological automation on various work activities and modeling different scenarios for technology adoption.
At that time, they estimated that workers spent at least half their time adjusting existing technologies to automate processes, which is what we refer to as the potential for technological automation.
Experts also simulated a range of possible scenarios to determine the adoption rate of these technologies and their impact on work activities in the global economy.
First, the large-scale application of technology will not happen overnight. It takes time to translate laboratory technologies into the automation of specific work activities.
At the same time, if the cost of automation exceeds that of human labor, it is clearly not feasible.
Finally, even if it is feasible, widespread adoption on a larger scale will take time.
The focus of the report lies precisely here: the potential of generative AI in automating production and daily life, and how much it can improve work efficiency.
The report estimates that, based on the current performance of generative AI, its capabilities in various areas will reach human-level performance faster than previously anticipated, as shown in the figure below.
Previously, the research institute believed that 2027 was the earliest possible year for the technology to achieve intermediate-level human natural language understanding capabilities. However, in the latest report, this timeline has been moved up to 2023.
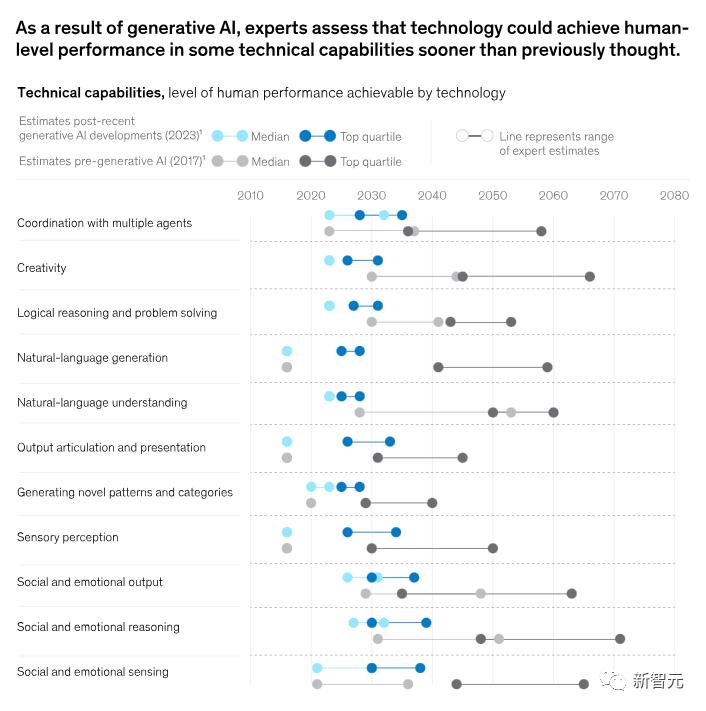
In theory, by integrating existing technologies, the total proportion of automation has now increased from about 50% to 60-70%.
Moreover, due to the rapid development of generative AI's natural language capabilities, the growth curve of technological potential is quite steep.
The following images show the predictions from 2017 and the latest forecasts. From the curves, it is easy to see how the word 'optimistic' is written.
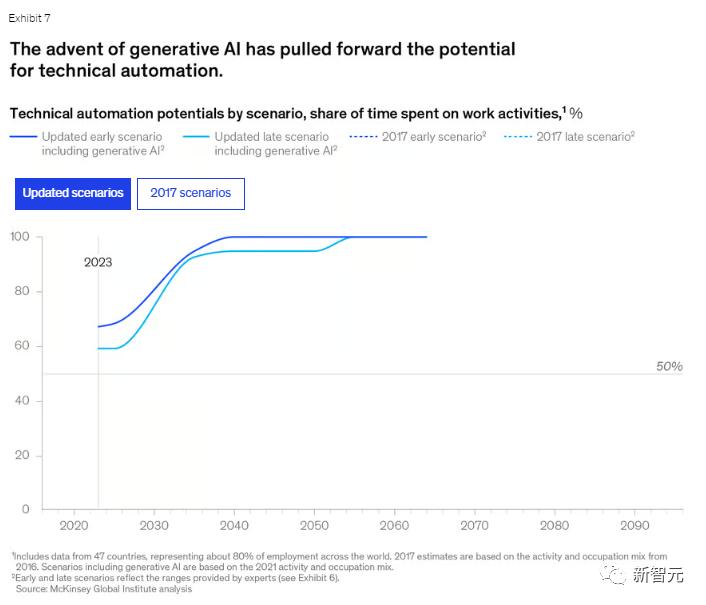
Latest Forecast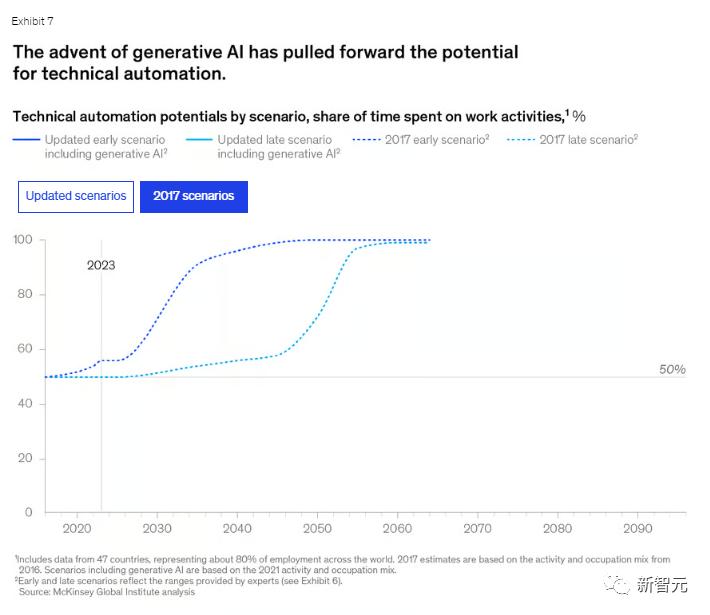
2017 PredictionThe image below shows the report's curve on how much change will occur in workers' daily activities, with the latest forecast above and the 2017 prediction below.
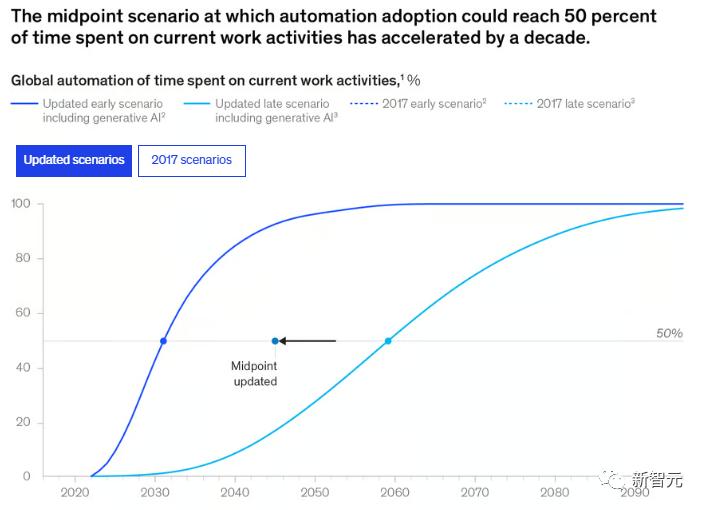
Latest Forecast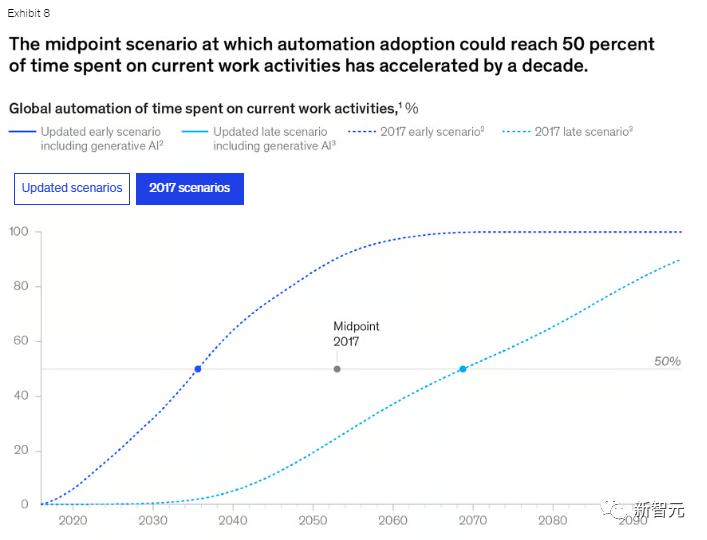
2017 ForecastExperts predict that generative AI may have the greatest impact on knowledge work, particularly activities involving decision-making and collaboration, which previously had the lowest automation potential, as shown in the figures below.
The report estimates that the potential for automation of professional expertise has surged by 34 percentage points, while the automation potential for management and talent development has risen from 16% in 2017 to 49% in 2023.
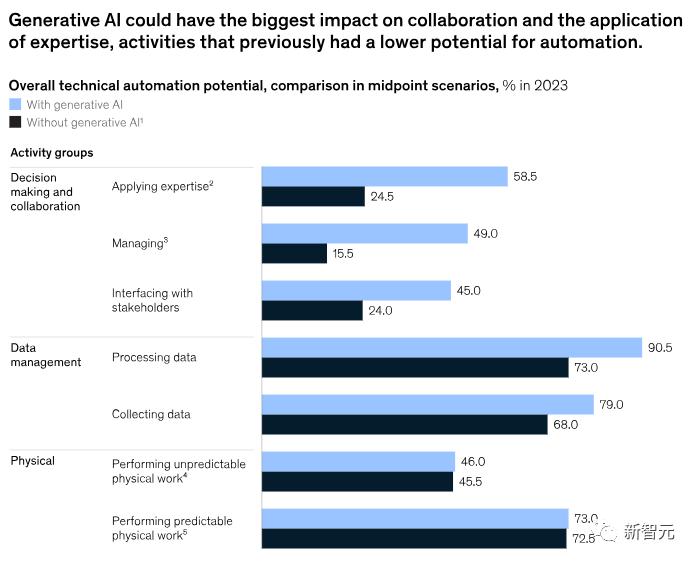
Additionally, generative AI can comprehend natural language and apply it to various activities and tasks, which largely explains why its automation potential is so substantial.
In the economic sector, approximately 40% of workers' activities require at least a median level of human natural language understanding.
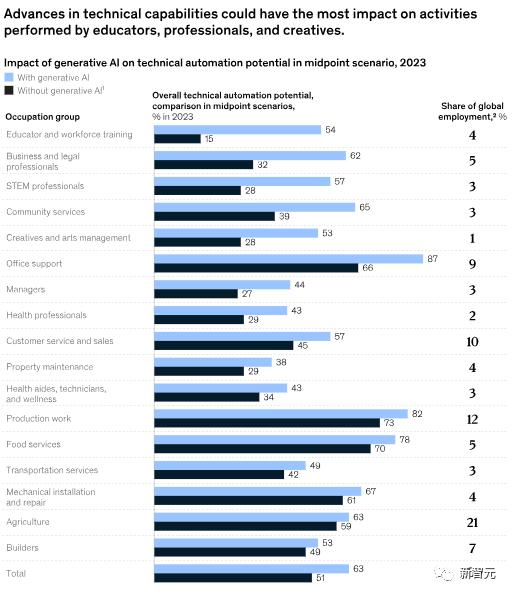
Consequently, many job activities involving communication, supervision, documentation, and human interaction could potentially be automated through generative AI. This accelerates workforce transformation in professions like education and technology, where automation potential was previously expected to emerge later, as shown in the figure below.
Beyond these points, the McKinsey report also analyzes the topic from other dimensions.
Due to space limitations, we won't enumerate them all here.
The above analysis can be said to focus entirely on the overall landscape of the industry.
To make the report more grounded, the final section discusses the impact of generative AI on individuals and how each of us should respond.
The report states that as new technologies develop, stakeholders must take action to prepare for opportunities and risks.
The main risks of concern are also those we frequently discuss, such as hallucination issues and the intellectual property rights of data used in training.
The report predicts that, under median forecasts, at least one-quarter to one-third of jobs will change in the next decade. The responses required will vary significantly depending on individuals' roles.
For company and business leaders, the question is how to leverage the potential value of generative AI while managing its risks.
In the coming years, how will generative AI and other AI technologies transform the professions and skill sets required for a company's workforce? How will companies implement these changes in hiring plans, retraining programs, and other aspects of human resources?
Can companies play a role in ensuring the technology is not used in ways that could harm society?
How can enterprises transparently share their experiences in promoting the use of generative AI within and across industries with the government and society? These are questions that managers need to explore.
For policymakers in government departments, what does generative AI mean for future workforce planning? How can necessary policy support be provided to workers as their activities evolve over time? Can new policies be formulated or existing ones revised to maximize the social value of AI?
Finally, as individuals—workers, consumers, and citizens—how should we engage with the development of new technologies? Where can we obtain accurate and unbiased information? How can individuals strike a balance between the convenience and the impact brought by generative AI? As individuals, how can we voice our concerns in decision-making processes?
Numerous issues await our in-depth consideration.
In simple terms, this report comprehensively examines the significant impact of the generative AI boom on our society, particularly in economic terms.
