The Future of Generative AI in Wealth Management
-
Looking at the major technology trends and investment hotspots in the first half of 2023, both domestically and internationally, there is no doubt that generative artificial intelligence (hereinafter referred to as 'generative AI') is one of the most prominent technologies. With the emergence of ChatGPT, this emerging technology has entered an unprecedented boom. Industries across the board are engaging in discussions on related topics, not to mention the rush of tech giants and AI companies eager to partake in this technological feast. Industry leaders and media have even likened the wave of generative AI to the opportunities presented by the mobile internet era, further highlighting its immense potential value and influence.

Compared to traditional AI, generative AI has four core advantages that make it stand out: automation and efficiency enhancement, personalization and customization, creativity and innovation, as well as explainability and transparency. This is particularly important for fields like finance and healthcare that require explainability, as it helps build trust, meet regulatory requirements, and makes it easier for people to accept and adopt system decisions.
In short, generative AI can create tremendous value for industries worldwide in three key ways: improving production efficiency, driving innovation, and reshaping competitive landscapes.
McKinsey predicts that AI as a whole will contribute up to $25.6 trillion in positive economic impact globally, with generative AI alone accounting for $7.9 trillion—equivalent to 8% of the current global GDP.
Generative AI has captured the attention and imagination of people worldwide due to its broad utility—almost anyone can harness its 'superpowers' of understanding natural language and creating content. This makes generative AI particularly advantageous in enhancing industry productivity and driving product innovation, with the potential to disrupt existing paradigms across global sectors in the future.
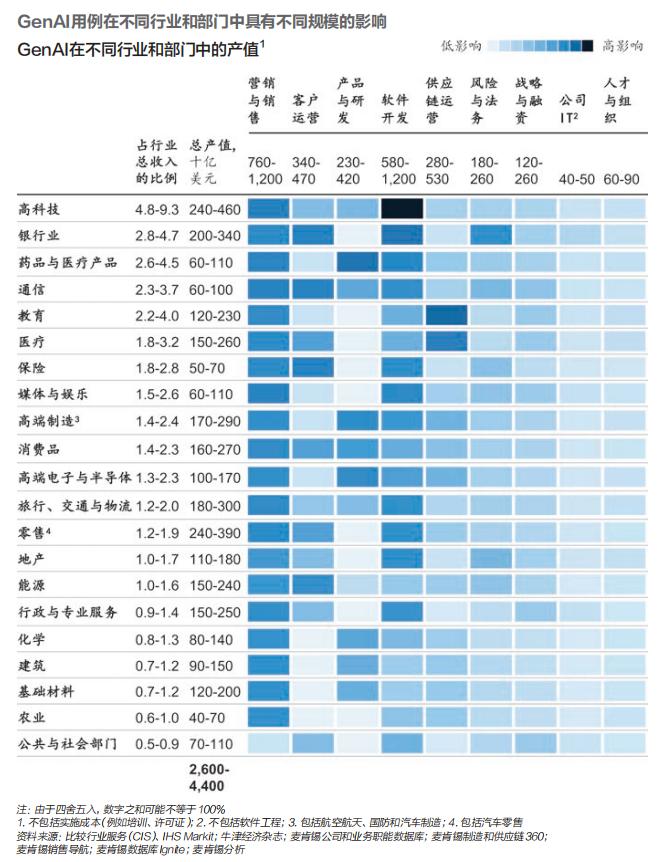
From an industry perspective, the three sectors where generative AI generates the most value are high-tech, banking, and retail. McKinsey estimates that by 2032, generative AI will add approximately $200 billion to $340 billion in annual value to the global banking sector (including asset and wealth management, collectively referred to as 'asset management'), accounting for 2.8% to 4.7% of the industry's annual revenue. Combined with the expected $50 billion to $70 billion in annual value from generative AI in the insurance sector (about 1.8% to 2.0% of industry revenue), the total value pool for generative AI applications in the financial industry (banking, insurance, and asset management) is projected to be $250 billion to $410 billion.
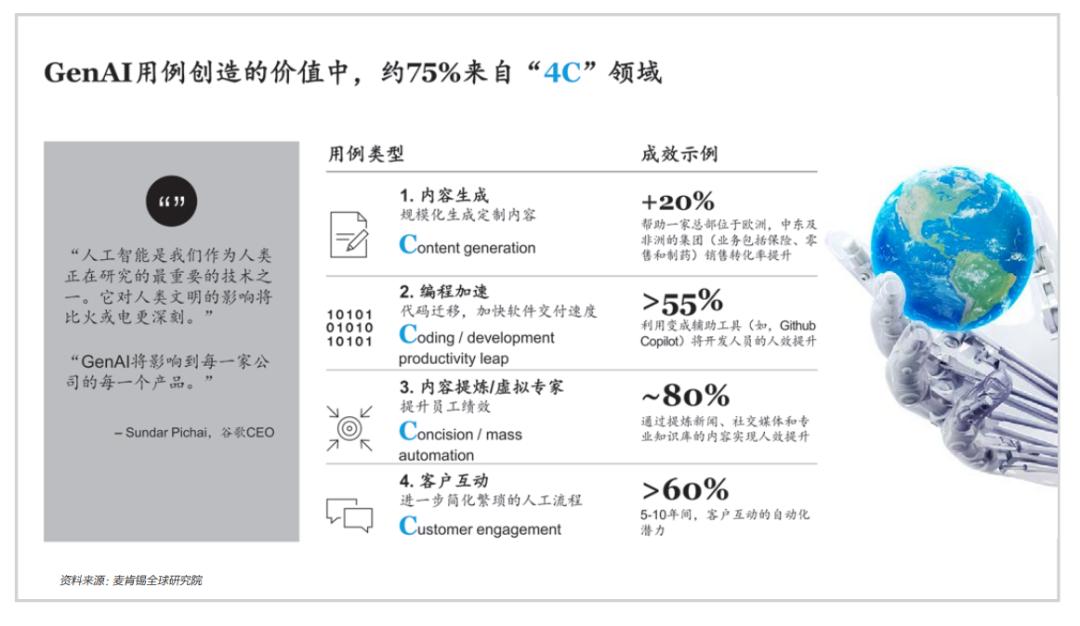
This demonstrates that, in terms of both absolute value and relative growth potential, the financial industry is one of the most promising sectors for generative AI applications. So, how does the dazzling array of generative AI technologies create value by aligning with industry characteristics? McKinsey observes that there are currently four mainstream application methods, which together account for 75% of the total benefits generated by generative AI in finance. These are summarized as the '4Cs': Content refinement/virtual experts (Concision), Customer engagement, Content generation, and Coding acceleration.
By sector, in banking, generative AI can automate repetitive and tedious financial tasks, improving efficiency, reducing costs, and freeing up employees for higher-value work. Through virtual experts, frontline bank staff can extract insights from unstructured data, interpret text, and quickly access relevant information like product guidelines and policies, boosting efficiency by up to 60%.
Other typical use cases include:
- Transaction processing: Automating financial transactions such as order processing, settlement, and clearing.
- Financial report generation: Automatically collecting, organizing, and analyzing financial data to produce accurate, timely reports compliant with accounting standards, reducing preparation time and human errors.
- Risk assessment and compliance checks: Automatically analyzing large volumes of financial data to identify potential risks and ensure compliance.
In customer interactions, generative AI systems learn from vast professional knowledge and human experience to provide personalized solutions. Financial institutions can offer more tailored, efficient, and satisfying services. For example, chatbots can handle customer outreach and data collection, with over 80% of customer interactions expected to be automated in the next 5–10 years. Other use cases include intelligent assistants, personalized recommendations, and sentiment analysis.
In content generation, generative AI analyzes text, images, and audio to create new content, speeding up financial firms' R&D processes. Examples include generating market analysis reports, personalized investment insights, drafting contracts and tender documents, and creating marketing materials for banks, insurers, asset managers, and brokerages.
In programming acceleration, generative AI interprets and generates code, automating snippets, templates, and algorithms to speed up software development and reduce errors—critical for quantitative trading and risk management in finance.
From the perspective of banking business functions, generative AI use cases have the greatest impact on four key areas: frontline distribution, customer operations, technology, and legal/risk/compliance/fraud departments, accounting for approximately 70% of its overall value potential in banks. The use of generative AI tools can enhance customer satisfaction, improve decision-making, elevate employee experience, and reduce risks through better monitoring of fraudulent activities.
In the insurance sector, as a vital component of the financial industry, generative AI brings significant value to both property and life insurance when viewed through the 4C lens. This includes: improvements in software development speed and quality, substantial efficiency gains for claims adjusters, enhanced productivity for insurance brokers and customer value propositions, and notable improvements in policyholder experience.
McKinsey's observations show concrete results: approximately 25% cost savings in complex claims (e.g., litigation claims), about 18% improvement in fraud detection accuracy, automation of 99% of underwriting processes through generative AI solutions, and potential 10%-20% reduction in insurers' underwriting costs.
In asset management, McKinsey has identified four key applications (4C) of generative AI. For content distillation and virtual expertise, it generates insights from unstructured data to drive investment actions like identifying investment targets. For instance, a major U.S. financial information provider developed its own GPT model trained on both domain-specific financial data and general data for financial Q&A and report analysis.
In programming acceleration, a multinational investment bank uses ChatGPT-style tools to assist developers in coding. For content generation, a North American asset manager employs ChatGPT to accelerate marketing collateral creation and develop data visualization tools. In user interaction, one of America's largest fund management companies launched AI-assisted registration technology using proprietary NLP models for creating, reviewing, and approving public communications. These generative AI applications span asset management functions while addressing needs of both investors and internal staff.

At its core, generative AI can deliver significant value to the financial industry due to four long-standing characteristics of the sector, using banks as an example:
- Legacy IT Infrastructure: Banks have invested heavily in technology for decades, accumulating substantial "technical debt" and siloed, complex IT systems.
- Large Customer-Facing Workforce: The banking industry relies on a vast number of customer service representatives.
- Document-Intensive Operations: Generative AI can assist employees across the organization in tasks like drafting emails, creating business presentations, and more.
- Strict Regulatory Environment: As a highly regulated industry, banking faces extensive risk, compliance, and legal requirements.
In summary, for financial institutions, generative AI applications can:
- Improve productivity by reducing human errors, saving time and resources.
- Enhance innovation, delivering better products and superior service experiences to end-users.
With the rapid growth of generative AI, its market size is expanding significantly, attracting substantial investment. According to Bloomberg data:
- 2022 market revenue: $40 billion
- Projected 2027 revenue: $399 billion
- Projected 2032 revenue: $1.304 trillion
- CAGR (2022–2032): 42%
In China, per the China AI Digital Outlook 2021–2025:
- 2022 market size: ~¥66 billion
- CAGR (2020–2025): 84%
- By 2025, China is expected to account for 14% of the global market ($217 billion).
Thus, generative AI not only creates immense economic value globally but also presents significant investment opportunities within the industry itself.
The generative AI value chain comprises six key segments: specialized hardware, cloud platforms, foundational models, model hubs and MLOps, applications, and services. While the thriving technology presents significant opportunities across the entire value chain, research indicates substantial variations in market potential among different segments. Certain areas exhibit formidable barriers to entry for newcomers and small businesses due to resource requirements, specialized expertise, and first-mover advantages.
From 2022 to 2035, the global market growth will primarily stem from training-side hardware, advertising applications, and software. Infrastructure services are projected to achieve a 60% compound annual growth rate (CAGR), contributing $244.8 billion in incremental value, while advertising applications are expected to grow at 125% CAGR, adding $192.4 billion.
Key market opportunities in the generative AI value chain include:
-
Specialized Hardware: The computational infrastructure for model training and inference presents high market barriers, currently dominated by major players. The core of computational hardware consists of processing chips like GPUs and TPUs.
-
Cloud Platforms: These platforms provide access to computational infrastructure and support generative AI workloads, with market share being highly concentrated among a few providers.
-
Foundational Models: As the central component of the generative AI value chain, this segment requires specialized knowledge and significant investment. The general large model sector shows a trend toward market concentration, while industry-specific models still present untapped opportunities.
4. Model Centers and MLOps: Tools for hosting, fine-tuning, and deploying models, where major players and independent vendors compete with differentiated offerings. Model centers and MLOps handle two essential tasks for building applications on foundation models: first, model repositories that provide storage and access to foundation models; second, specialized MLOps tools for fine-tuning and deploying foundation models into applications.
5. Applications: End-user applications based on fine-tuned large models represent the sector with the greatest opportunities for startups. Approximately half of generative AI unicorns have emerged in this market. We anticipate that in the short term, applications developed for vertical industries and specific functions, based on meticulously fine-tuned models, will be the first to stand out.
6. Services: Integrated solution providers offering value-added services based on model products are dominated by large corporations, but niche markets still offer opportunities for small and medium-sized players.
First is the transformation of operational models. Scaling GenAI requires enterprises to undergo a comprehensive transformation of their operational models, embedding AI into every aspect of their business. When implementing GenAI applications at scale, a successful operational model should cover six key areas: strategic roadmap, talent, operational model, technology, data, and technology application and change management.
Generative AI is evolving rapidly, and CEOs are exploring its business value and potential risks. CEOs play a crucial role in driving corporate focus on generative AI. As they embark on this journey, CEOs should keep in mind strategies that align with the responses required during previous technological waves.
However, generative AI also brings unique challenges, including its unprecedented development speed compared to previous technological transformations and the resulting difficulty in response.
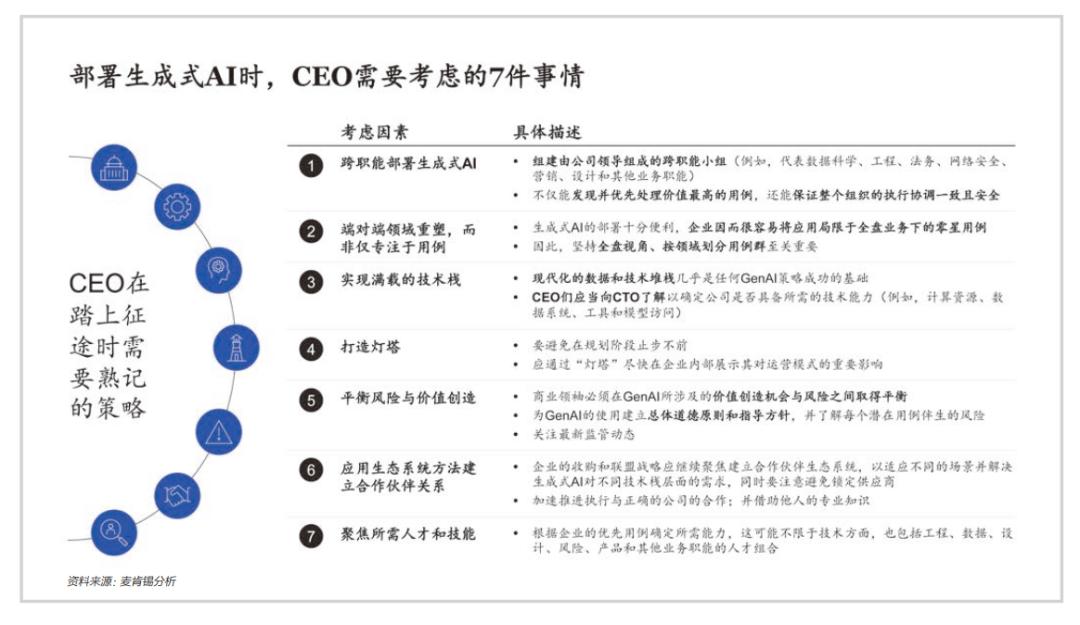
To this end, we provide a core summary of generative AI for CEOs to reference (see image above).
Before deciding to implement generative AI, companies should consider the significant time and resource costs associated with starting from scratch and repeated trial and error. They can also leverage the expertise of professional organizations to accelerate the deployment of generative AI, utilizing third-party technology, knowledge, and experience to avoid detours and pitfalls, thereby achieving value creation goals more quickly and cost-effectively.
Additionally, it is worth noting that while generative AI provides new growth drivers for various industries, it also carries certain negative impacts. Financial institutions, in particular, need to be vigilant about three key risks when applying generative AI: model hallucinations, malicious use, and information leaks. Businesses must take these risks seriously and actively implement measures to properly prevent and manage them, minimizing potential risks while maximizing value release.
