The Past and Present of OpenAI
-
The Past and Present of OpenAI
OpenAI's success is not accidental but the result of systematic evolution. This article will explore its journey from four dimensions: founding background, technological evolution, product breakthroughs, and business models, helping you understand how an AI company transitions from concept to reality, from models to ecosystems.

This article provides a comprehensive overview of OpenAI's development, discussing its corporate structure, technological advancements, business models, financials, valuation, and future prospects, with extensive technical details.
The original article includes over 20 images, some of which I've annotated. Enjoy, and feel free to like, follow, and bookmark. (I’ll later update with a list of books recommended by Jensen Huang—this remarkable 62-year-old entrepreneur, with 32 years in the industry, has only endorsed seven books, all of them classics. Stay tuned.)
Table of Contents
- Pre-OpenAI Era (Before 2015)
- The Founding of OpenAI
- OpenAI’s Technology
- OpenAI’s Business Model
- Market Data and Competitive Landscape
- OpenAI’s Future
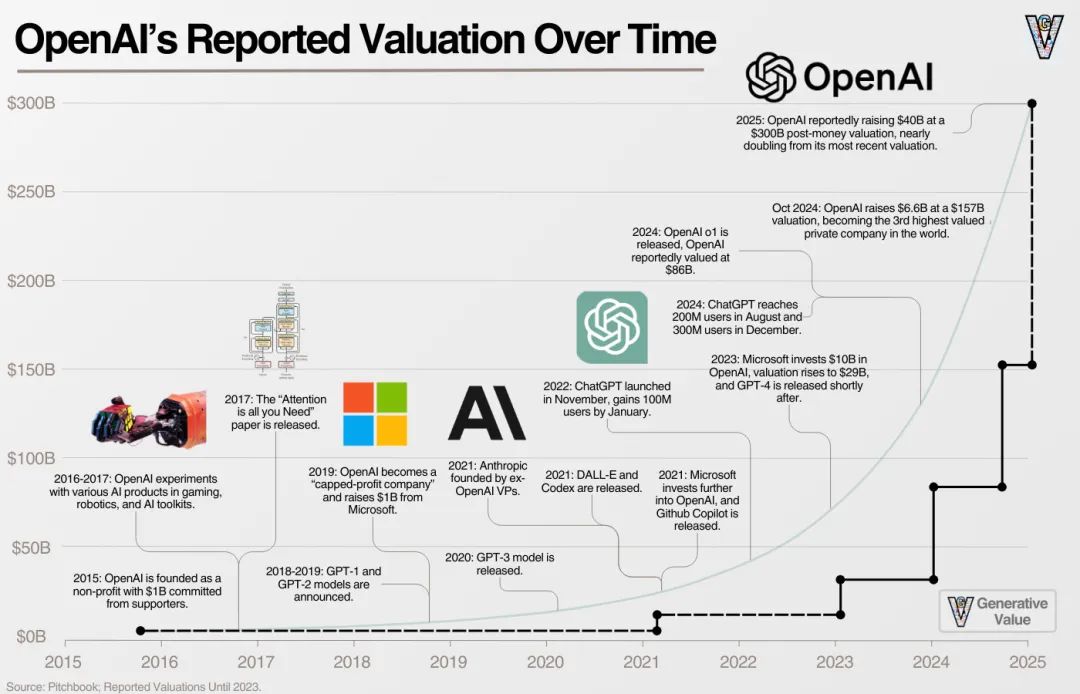
This chart illustrates OpenAI’s valuation growth trajectory since its founding in 2015, showing exponential growth from a modest initial valuation.1. Pre-OpenAI Era (Before 2015)
Before OpenAI’s inception in 2015, three key factors laid the groundwork for its creation:
1.1 The Rise of Deep Learning
In 2012, a team comprising Ilya Sutskever (OpenAI’s former Chief Scientist, now founder of Safe Superintelligence), Alex Krizhevsky, and AI pioneer Geoff Hinton achieved a breakthrough in a competition, significantly surpassing previous benchmarks.
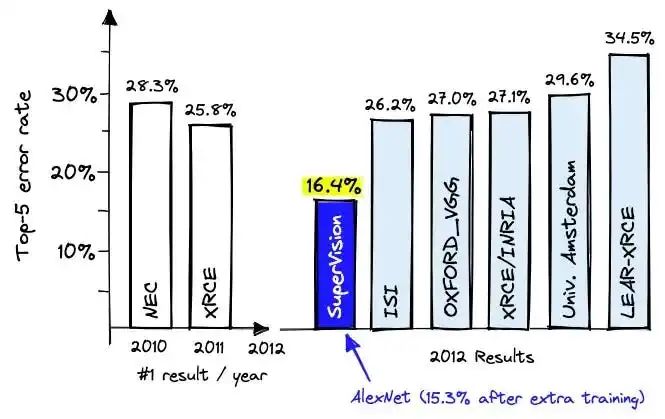
Comparison of error rates in the ImageNet competition (2010–2015), highlighting the 2012 breakthrough in deep learning models. Lower bars indicate better performance.1.2 The AI Talent Duopoly of Google/Meta
After the ImageNet breakthrough, Facebook and Google dominated AI talent recruitment, forming a duopoly. Google’s acquisition of DeepMind alarmed Silicon Valley, prompting two individuals—Elon Musk and Sam Altman—to envision an alternative: a nonprofit AI research lab.
1.3 Sam Altman’s Ascent
Sam Altman, now OpenAI’s CEO, rose to prominence as the face of the company post-ChatGPT. Previously, he led Y Combinator and was one of Paul Graham’s (author of Hackers & Painters) most admired entrepreneurs.
Paul Graham once said: “Sam Altman is one of the few founders I reference alongside Steve Jobs. For design questions, I ask, ‘What would Steve do?’ For strategy and ambition, I ask, ‘What would Sam do?’”
These three factors—technological breakthroughs, the need for an alternative to Google/Facebook, and the emergence of a visionary leader—culminated in a legendary meeting at Silicon Valley’s Rosewood Hotel.
2. The Founding of OpenAI
At that dinner, Elon and Sam pitched the idea of OpenAI to top AI researchers. Ilya Sutskever, OpenAI’s “AI genius,” was particularly drawn to the vision. Soon, Ilya and Greg Brockman (OpenAI’s “executor”) became its leaders, backed by $1 billion from Elon Musk, Peter Thiel, and Reid Hoffman. OpenAI’s mission was clear: AI could reshape the world, and its development should be guided by a nonprofit for humanity’s benefit.
Early projects included OpenAI Gym (reinforcement learning), OpenAI Universe (virtual environments), OpenAI Five (Dota 2 AI), and OpenAI Dactyl (robotic hand).
2.1 The Emergence of Transformers
In 2017, Google’s paper Attention Is All You Need introduced the Transformer architecture. Ilya recognized its significance immediately. Transformers revolutionized context-aware language processing by calculating word relationships and positions, enabling models to predict the next word probabilistically.
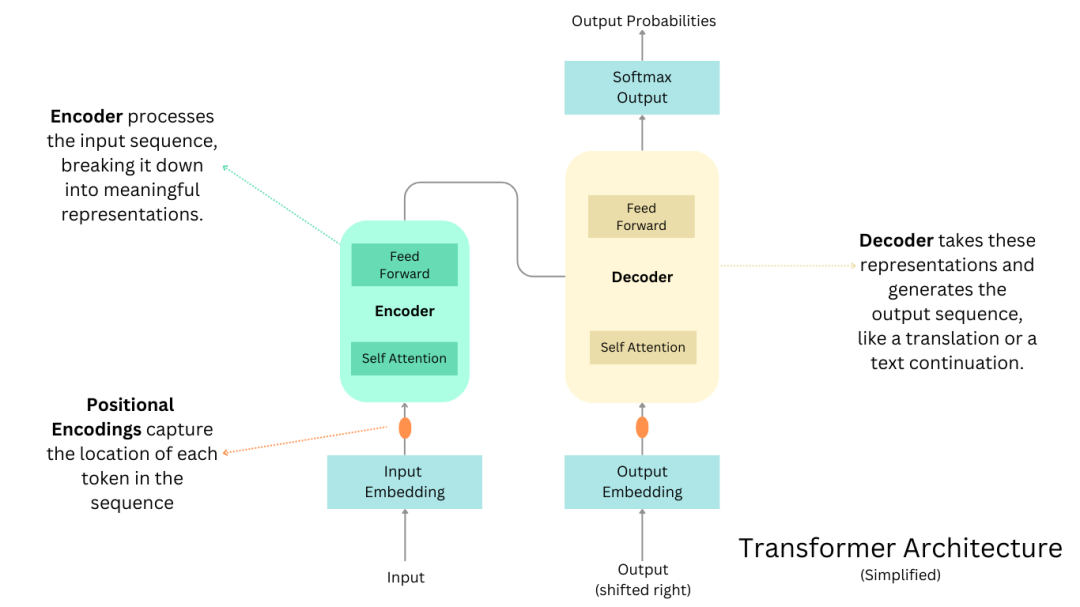
Simplified Transformer architecture, showcasing encoder-decoder self-attention mechanisms for contextual understanding.Key stages:
- Input Embedding: Tokens are converted to vectors with positional encodings.
- Encoder: Processes input context via self-attention and feedforward layers.
- Decoder: Generates output sequences using encoder representations.
- Output: Predicts the next word via probability distribution.
This breakthrough enabled GPT-1 (2018) and scalable AI learning.
2.2 From Nonprofit to Capped-Profit (2019–2022)
OpenAI’s shift to a capped-profit model sparked controversy, leading to Elon Musk’s departure. Scaling required massive resources, necessitating investor returns. In 2019, OpenAI LP (a capped-profit entity) was formed under OpenAI Inc. (nonprofit), securing $1 billion from Microsoft.
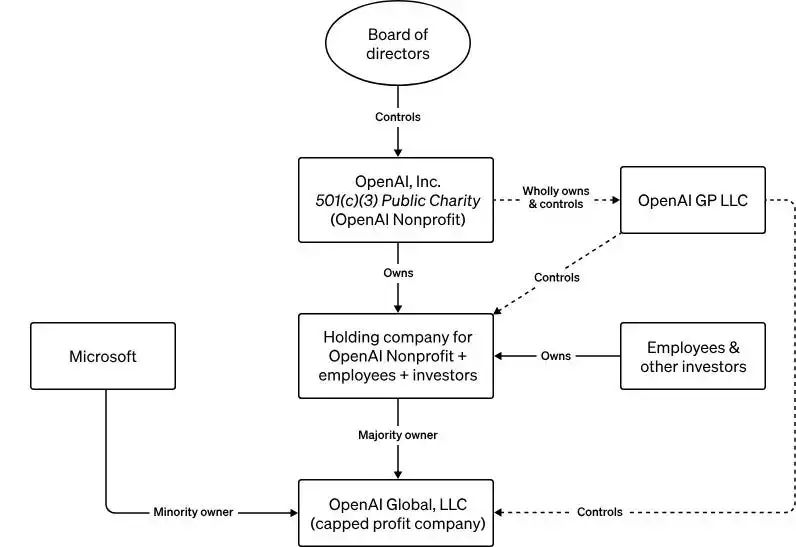
OpenAI’s dual structure: Nonprofit controls a profit-capped subsidiary.With funding, OpenAI released GPT-3 (2020), Codex (2021), DALL-E (2021), and ChatGPT (2022), igniting the AI revolution.
2.3 Chat With GPT-3.5
Sam Altman reflected: “In 2022, OpenAI was an obscure lab working on ‘Chat With GPT-3.5.’ We knew an AI tipping point would come—we just didn’t expect ChatGPT to be it.”
Microsoft seized the moment, investing $10 billion and integrating OpenAI tech across its products.
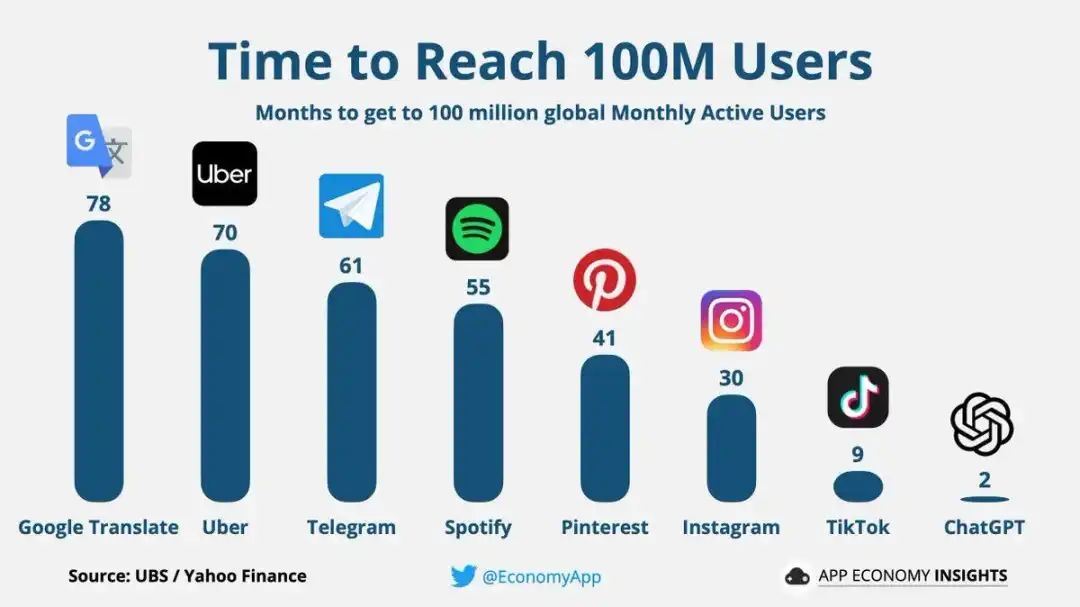
Since then:
- OpenAI became the face of AI.
- Sam Altman briefly left and returned.
- Competition surged (Anthropic, Meta, xAI, Google, DeepSeek).
- Revenue hit ~$4 billion annually (2024).
- ChatGPT reached 300M users.
OpenAI now stands at a crossroads:
- Nearing AGI development.
- Battling open-source rivals.
- Balancing governance, sustainability, and superintelligence.
3. OpenAI’s Technology
Understanding LLMs requires tracing AI’s evolution:
- Conceptualization → Deep Learning → Transformers → Early LLMs → ChatGPT → Reasoning → Agents.
3.1 AI Foundations
AI aims to automate human tasks, approaching human intelligence. Neural networks, with adjustable “nodes,” model complex patterns. More nodes/layers enable deeper learning.
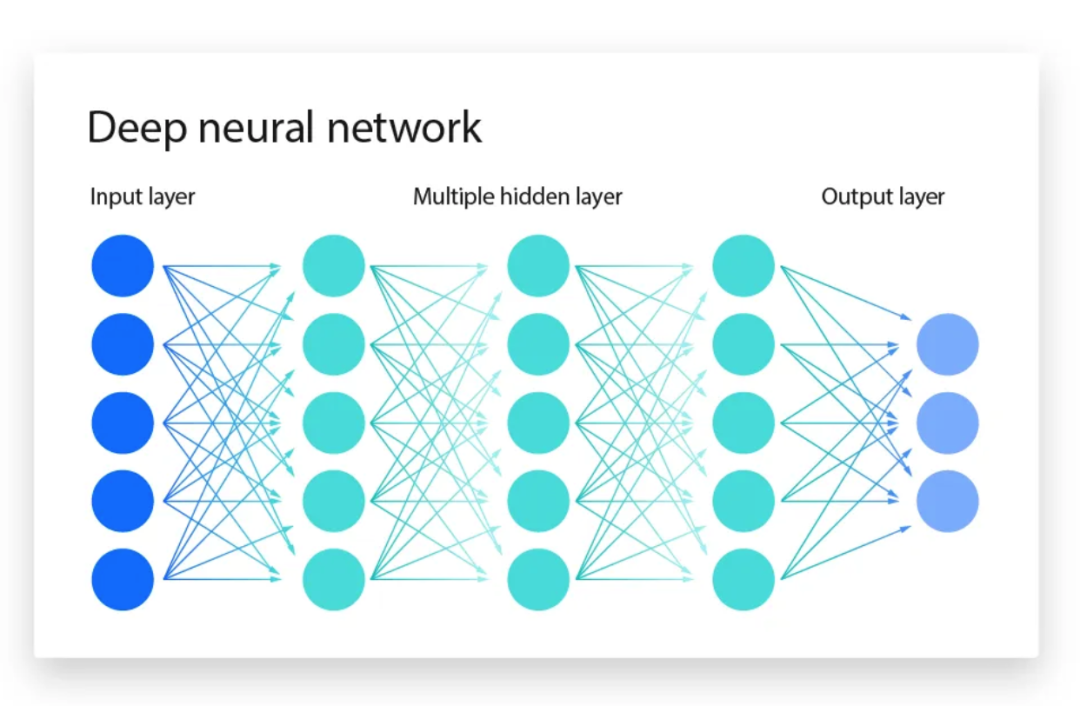
Multilayer neural network: Input → Hidden Layers → Output.GPU-powered big data fueled modern AI, exemplified by AlexNet (2012).
3.2 Modern AI: The LLM Black Box
Transformers (2017) integrated context via attention mechanisms. For example, “float” can mean “hover” or “ice cream drink,” depending on context.
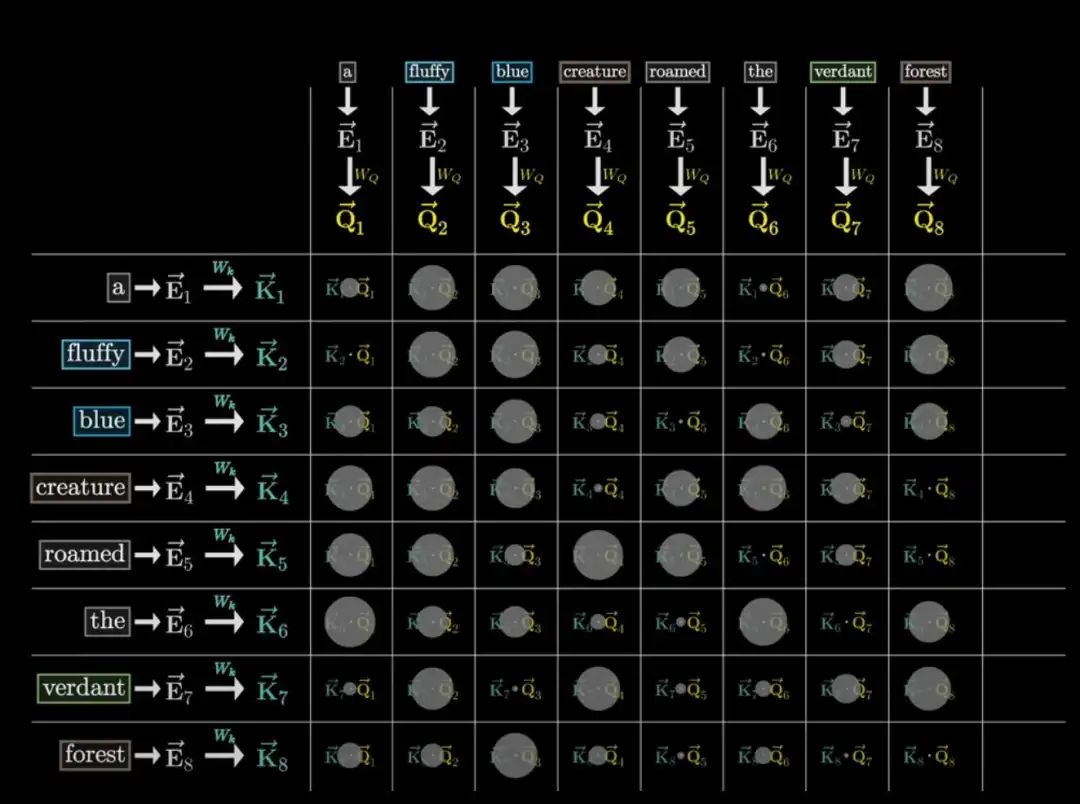
Attention grid showing word relationships.LLMs tokenize input, embed words, process via transformers, and output probabilities.
3.3 OpenAI’s Current Tech: Scale, Reasoning, Agents
Scaling—more data, GPUs, energy—drove ChatGPT’s quality. OpenAI categorizes AI into five tiers:
- Chatbots: Basic dialogue (e.g., ChatGPT).
- Reasoners: Logical problem-solving.
- Agents: Task execution (e.g., booking trips).
- Innovators: Creativity (e.g., art, science).
- AI Organizations: Collaborative agent networks.
Reasoning enables multi-answer evaluation, mimicking human thought. Agents transform AI from tools to doers.
OpenAI’s vision: AI progresses from chatbots to autonomous organizations.4. OpenAI’s Business Model
OpenAI is vertically integrated, with models as its core. Revenue stems from applications, while cost reduction drives margins.
4.1 Financials
- 72% of revenue comes from ChatGPT.
- 2024 revenue: ~$4B; losses: ~$5B.
- Gross margin: 41% (target: 67% by 2028).
- Path to $100B revenue: Dominance in AI agents.
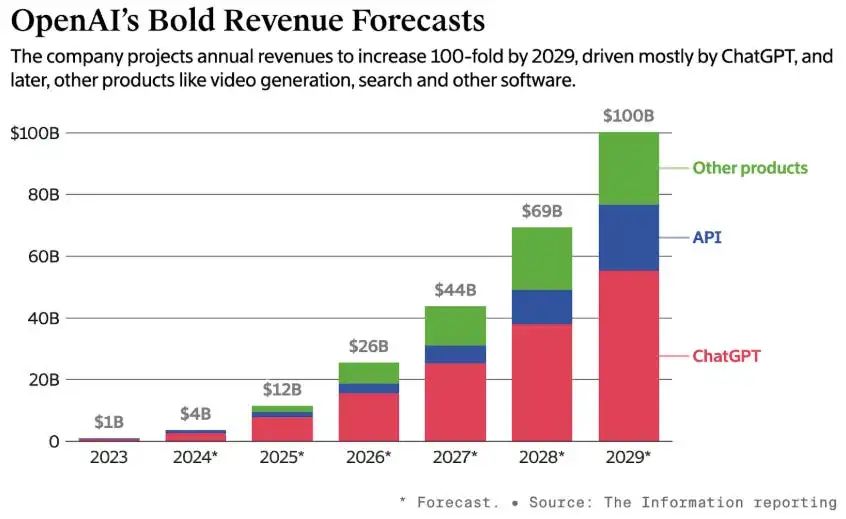
OpenAI’s growth hinges on agent-driven applications, not just APIs.4.2 Governance
OpenAI’s complex structure ensures nonprofit control:
- OpenAI Inc. (nonprofit) governs OpenAI LP (capped-profit).
- Microsoft holds ~49% stake, with profit caps.
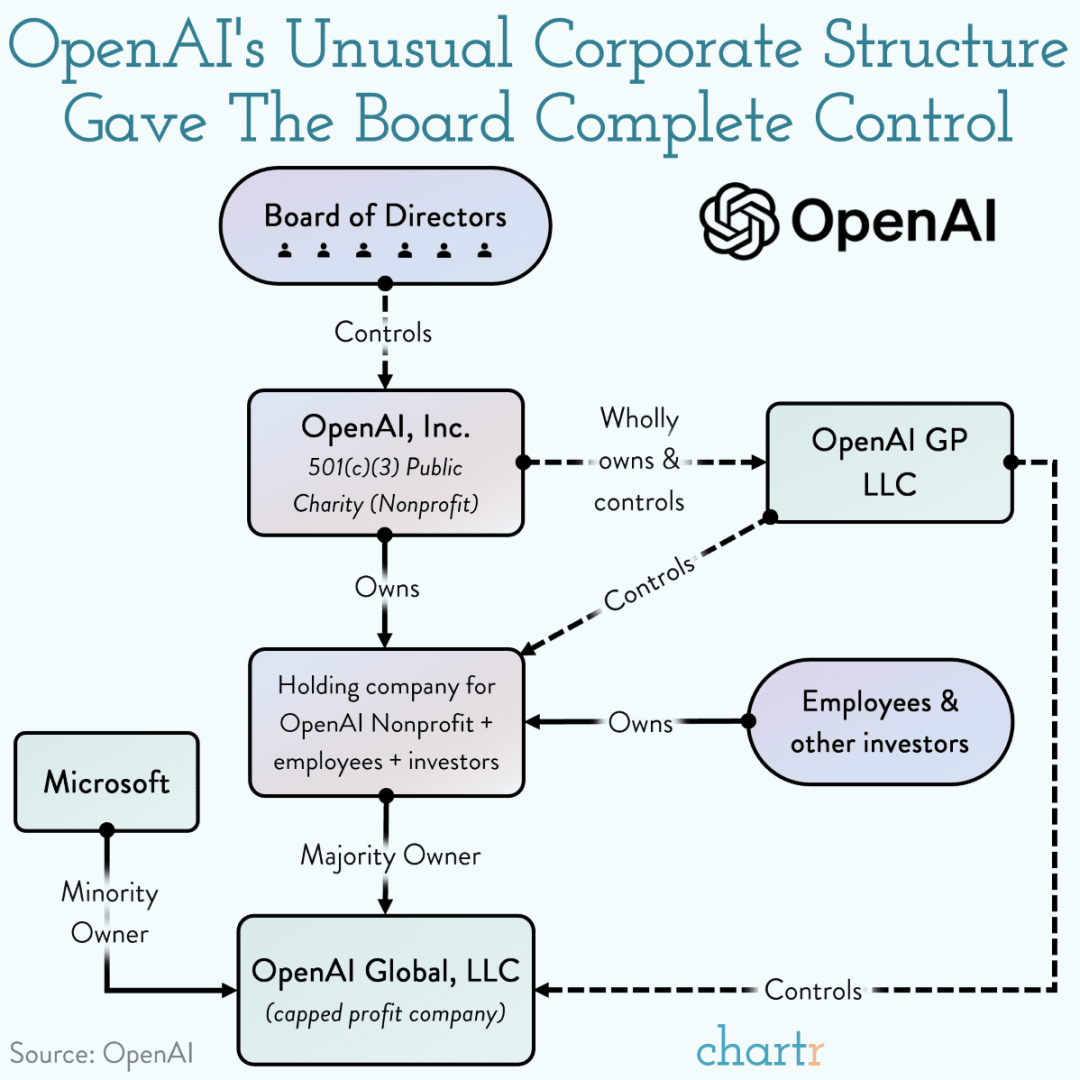
OpenAI’s governance: Nonprofit board controls profit-capped subsidiary.5. Market and Competition
- Benchmarks: Skepticism advised.
- Anthropic: $960M annual run rate (2024).
- OpenAI: $12B projected revenue (2025).
- Model commoditization pressures margins; apps are key.
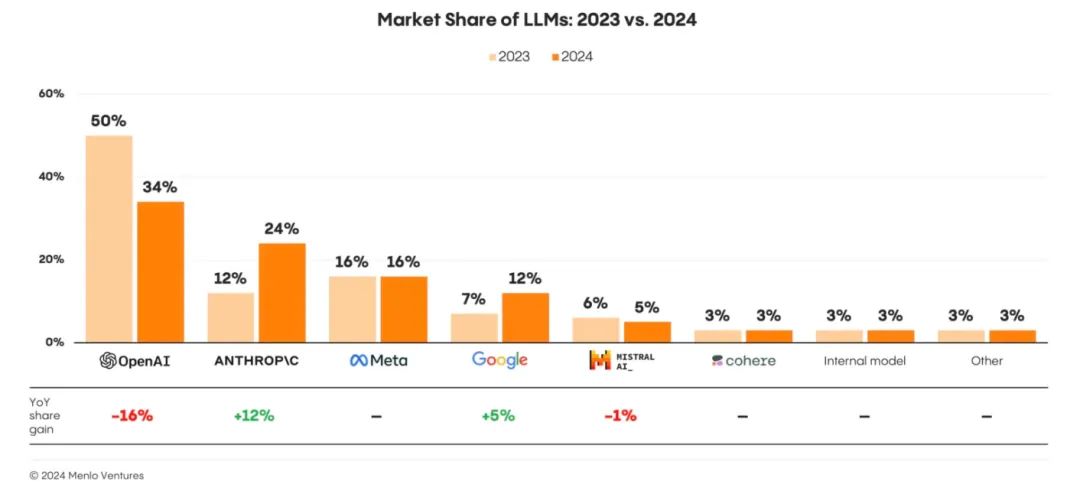
LLM market share shifts (2023 vs. 2024).6. OpenAI’s Future
Key variables:
- Cost Structure: Vertical integration (e.g., Stargate chips).
- Business Model: Monetizing beyond APIs.
- Market: AI’s trillion-dollar potential.
- Product: From information to action (e.g., Operator).
- Valuation: $157B (39x revenue) reflects long-term bets.
“If you aren’t willing to own a stock for 10 years, don’t own it for 10 minutes.”
OpenAI could become a trillion-dollar giant or face valuation corrections. Either way, it’s a defining company of the AI era.
Summary
- Deep learning + GPUs + big data = AI revolution.
- Transformers enabled context-aware language models.
- ChatGPT democratized AI.
- OpenAI is among history’s fastest-growing companies.
- Agents, reasoning, and voice/search expand ChatGPT’s utility.
- Model competition intensifies; apps sustain dominance.
- Vertical integration aims for full-stack AI leadership.
Fin.
